3D organ bioprinting with polymers : all you need to know
In the context of bioprinting, 3D printers use bioinks to print 3D organs which are prototypically similar to real organs. These 3D-printed organ-like structures have the potential to be used in vivo as organ transplants or in vitro in the
A comparison of 2D and 3D cell cultures
Cell culture is the process of growing cells outside of their natural environment, typically in a laboratory setting. It involves the cultivation of cells in a controlled environment, usually in a special liquid medium that provides the necessary nutrients and
Using Biopolymers And Micromachining Technology In Generating Multicellular Spheroids
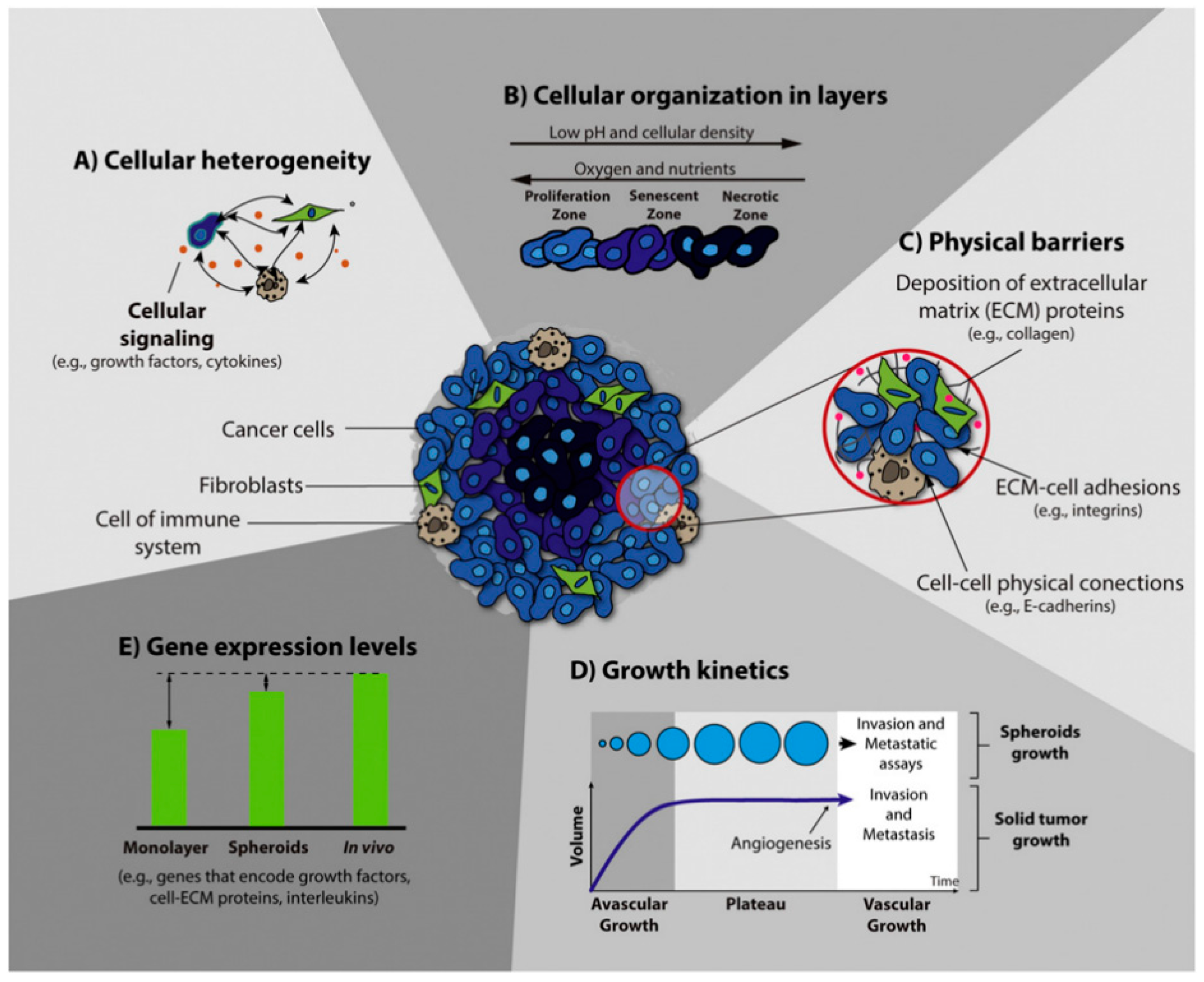
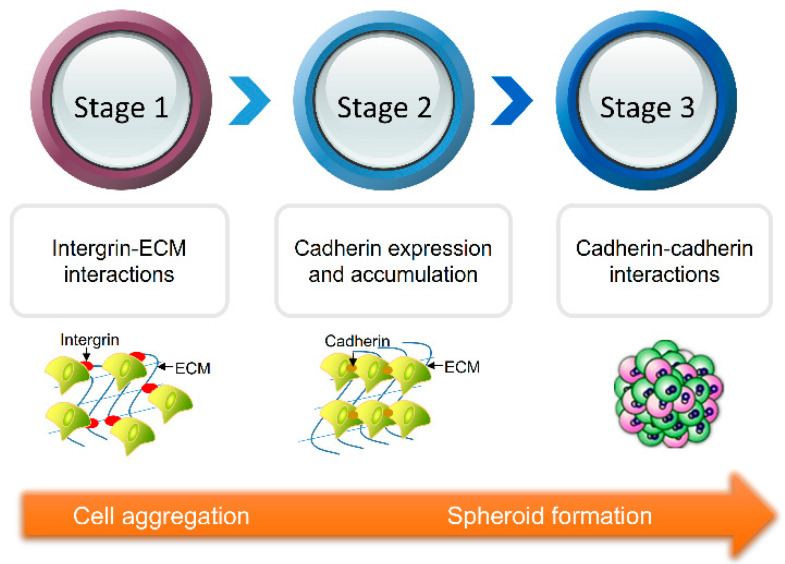
Multicellular spheroids (MCSs) are formed through spontaneous aggregation of cells in the presence of adhesion molecules known as cadherins (1). Decades of research have proved MCSs to be an efficient 3D cell culture model for a wide array of research.
Applications of Multicellular Spheroids (MCS)
Multicellular spheroids are formed through spontaneous aggregation of cells in the presence of adhesion molecules known as cadherins (1). Since its first implementation in 1952 (2), multicellular spheroids have served as an efficient 3D cell culture model for a wide
The importance of animal models in biomedical research
An animal model is a living, non-human species that imitates various facets of the biological processes found in humans. Rat and mouse animal models are essential in biomedical research in several contexts, including diabetes, cancer, drug assessments, and systemic autoimmune
Understanding the problems related to animal models
Animal models are non-human species that can be applied to reproduce the disease, diagnosis, and treatment progression that occurs in humans. Animal models are a fundamental tool in biomedical research and have many applications and advantages. However, many scientists are
The alternatives to animal testing
Animal models are used to study the effects of drugs and chemicals before testing them on human volunteers. Every year, millions of experimental animals are used all over the world for the advancement of research and development in medical technology.
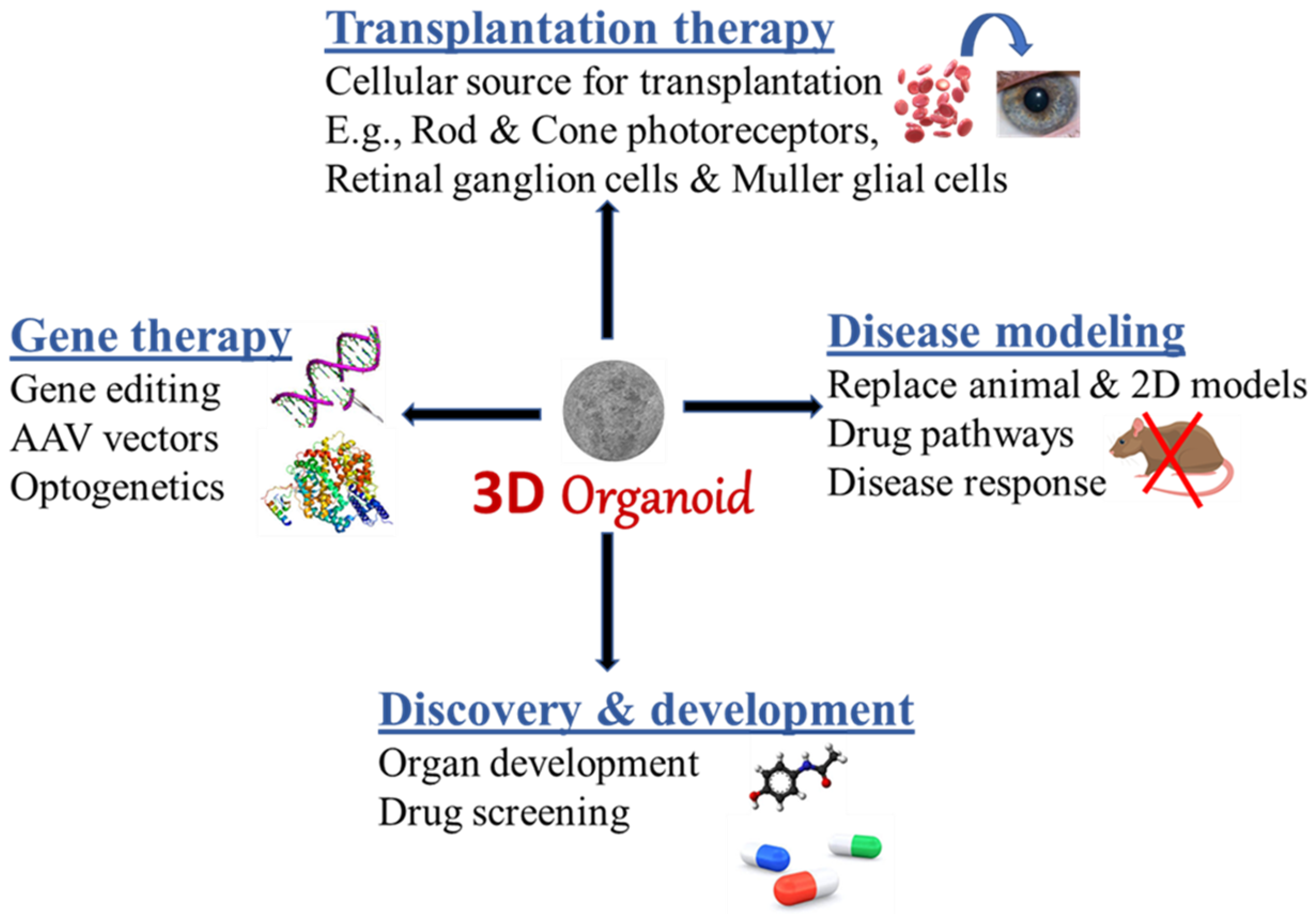
The Use Of Organoids In Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine refers to the method of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues, or organs with the aim to restore normal physiological functions (1). It has the potential to engineer damaged tissues and organs by triggering the
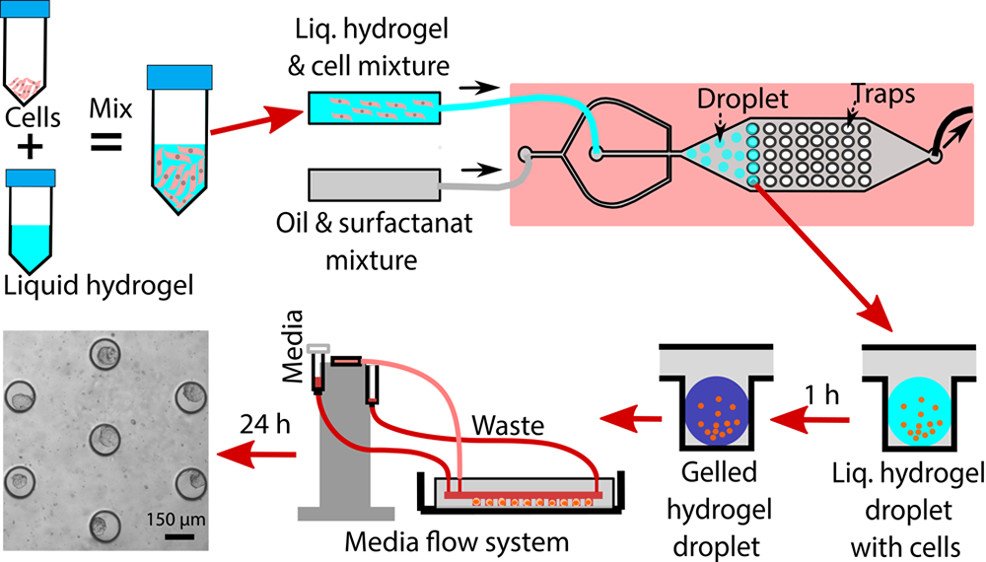
How to Generate Multicellular Spheroids
Since the introduction of monolayer cell cultures, cell culture methods have advanced exponentially in the past decade, moving from traditional 2D cell culture methods to 3D cultures. While 2D cultures are simple and allows for cell proliferation and differentiation, they
Introduction to fluorescence microscopy: Principle and types
Fluorescence is the property of some atoms and molecules to absorb radiation at a particular wavelength and subsequently emit light at a longer wavelength upon excitation of the atoms. A fluorescence microscope is a powerful optical tool that works based