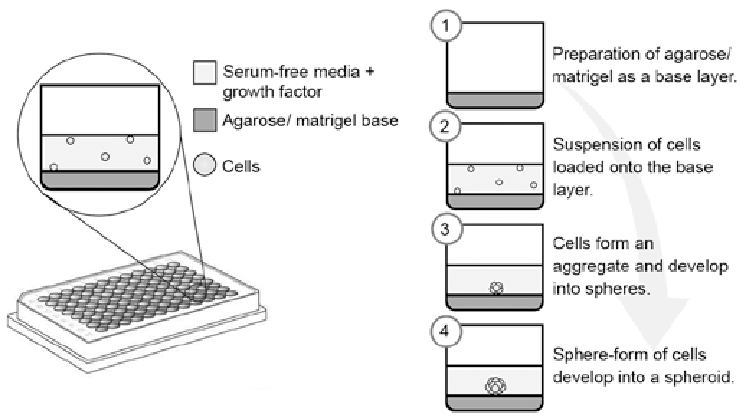
MULTICELLULAR THREE- DIMENSIONAL TUMOR SPHEROIDS
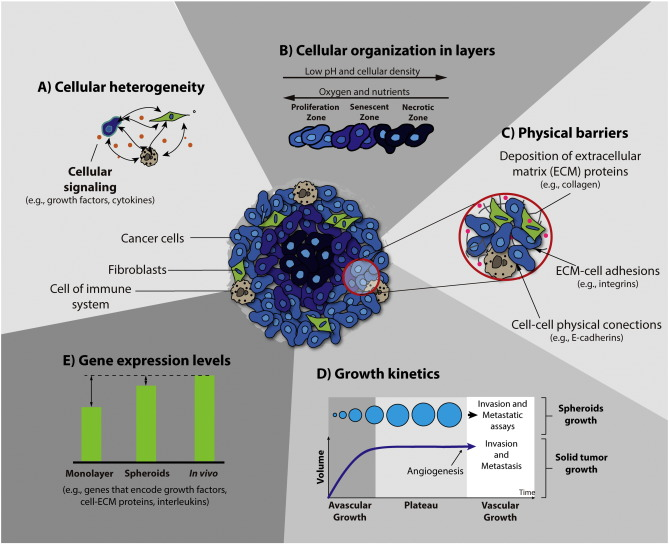
Multicellular tumour spheroids are three dimensional structures composed of cancer cells. They are formed from monolayer tumour cells when these are grown by various in vitro methods such as spinner flasks or rotation systems. Due to their cellular organisation in
Spheroid Culture Methods to Study Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines (pNEN)
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNEN) comprise of a group of rare tumours that originates from the islets of langerhans (1). Diagnosis of pNEN is often complicated by hormone hyper secretion that culminates in early clinical manifestations. 85% of patients do not
Spheroid cancer models to study drug efficacy
Spheroids formed within cancer cell lines mimic architecture and share the limited drug penetration properties since drugs are largely confined to outer cell layers. Spheroids, three dimensional architectures of cancer cells, are found in cancer patients with sizes of 250~
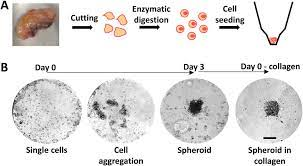
Three-dimensional self-assembling spheroid cultures: Human Neonatal keratinocytes
Spheroids are three-dimensional (3D) cell aggregates that can mimic tissues and mimic tumors. In recent years, there has been significant progress in development of in vitro aggregates. Epidermal spheroids provide a more representative view of the human skin than 2D
Three-dimensional skin spheroid cultures
Three-dimensional culture system provides unique platforms to study complex biological processes in vitro, particularly cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, and stress responses. While 3D spheroid cultivation methods are well established in certain tissue types such as mammary and colorectal epithelial cells,
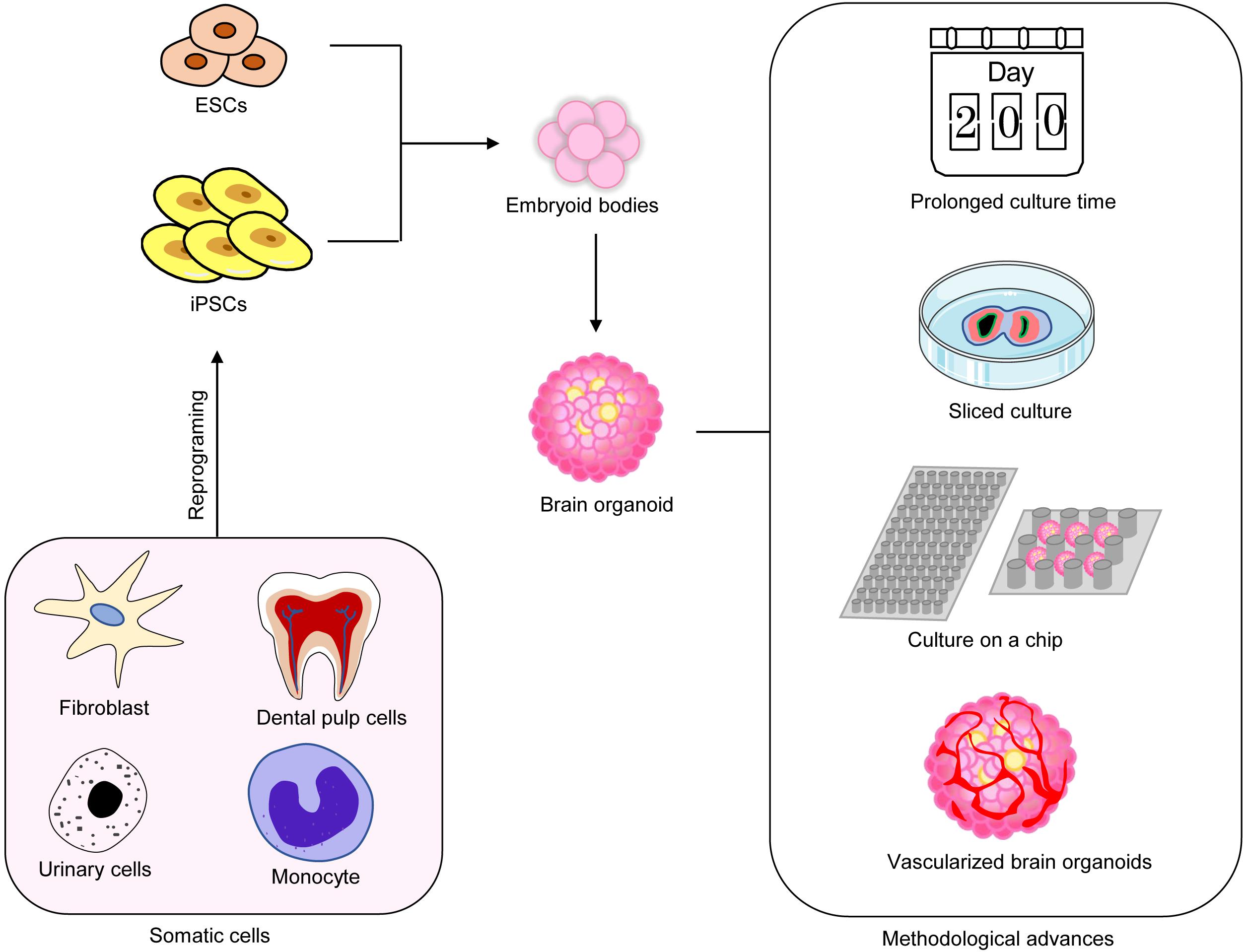
Genetically Modified Cerebral Organoids (Neocor)
Bian et al. recently developed protocols for genetically manipulating cerebral organoids to induce glioblastoma tumor growth named neoplastic cerebral organoids. This method uses CRISPR-based genome editing tools to create either oncogenic mutation or induce the expression of oncogenes to cause
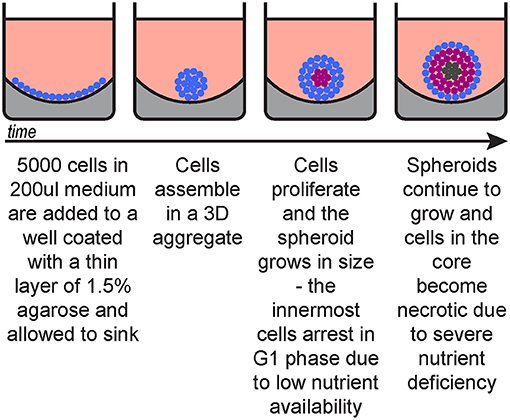
Factors Affecting Reproducibility of Uniform Spheroids in 384 well Plates
In the recent years 3D cultures of tumour cell lines have become an essential tool in cancer research and drug discovery processes. 3D cultures when compared with traditional 2D monolayer cultures, are able to produce cell cultures bearing close resemblance
Bioprinted Glioblastoma Organoids
Remarkable advancements have been made in the ability to print complex tissue, including 3D model of Glioblastomas and other cancers. In 2019 Yi et al. published a new approach for creating a 3D bio-printed glioblastoma-on-a-chip model from patient derived cells
3D Spheroid Technology Use in Drug Screening
Modern drug discovery processes has encountered significant setbacks in the past decades despite the technological advances made in analytical tools and research model development. This is primarily because of the use of inadequate biological models that do not mimic in-
Increasing Cellular Complexity Of Organoids
To address the modelling of cell-to-cell communication with the cell population and the development of vasculature in organoid system, significant progress has been achieved with blood vessels organoids which shows a great potential to impact research into vascular diseases. Despite