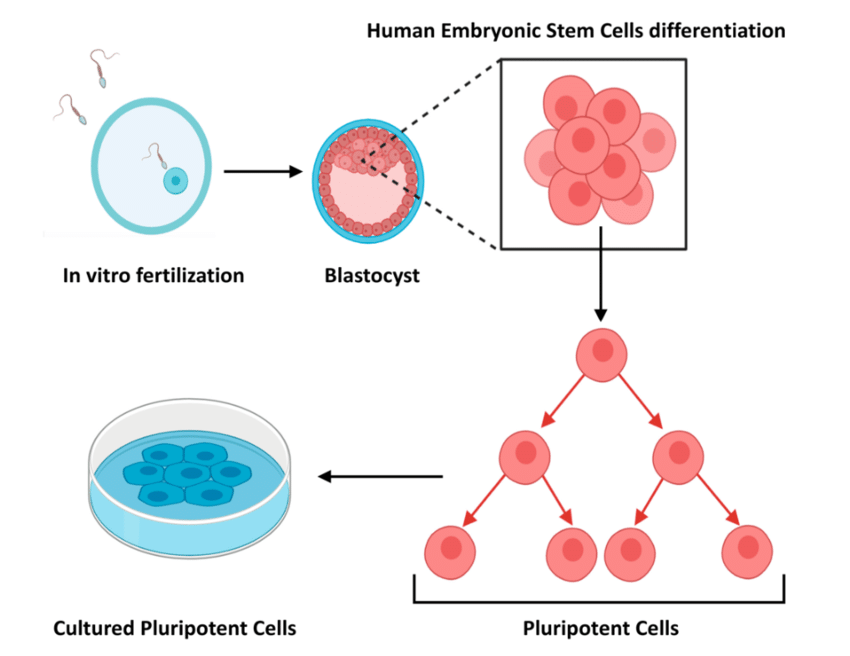
Embryonic stem cells as tools for investigating human development
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of human embryos in the blastocysts stage of development. They show an unlimited capacity to self-renew in culture systems both in vivo and in vitro.
Ribonucleic acid – An essential intermediate
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid that can be found in all living cells and has structural similarities to DNA. Unlike DNA, RNA is single-stranded. An RNA molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate group and the sugar
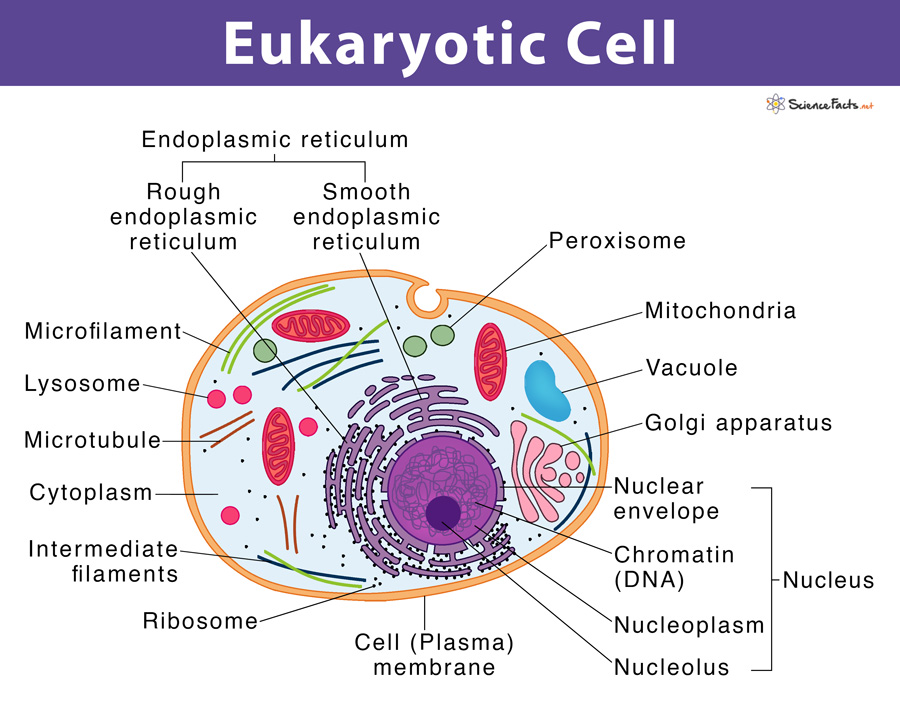
Introducing nucleic acids – Transfection of eukaryotic cells
Transfection is a widely used technique to introduce foreign nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It is an essential tool enabling studies on gene function and gene products in cells. Advances in research techniques have enabled the transfection of various types
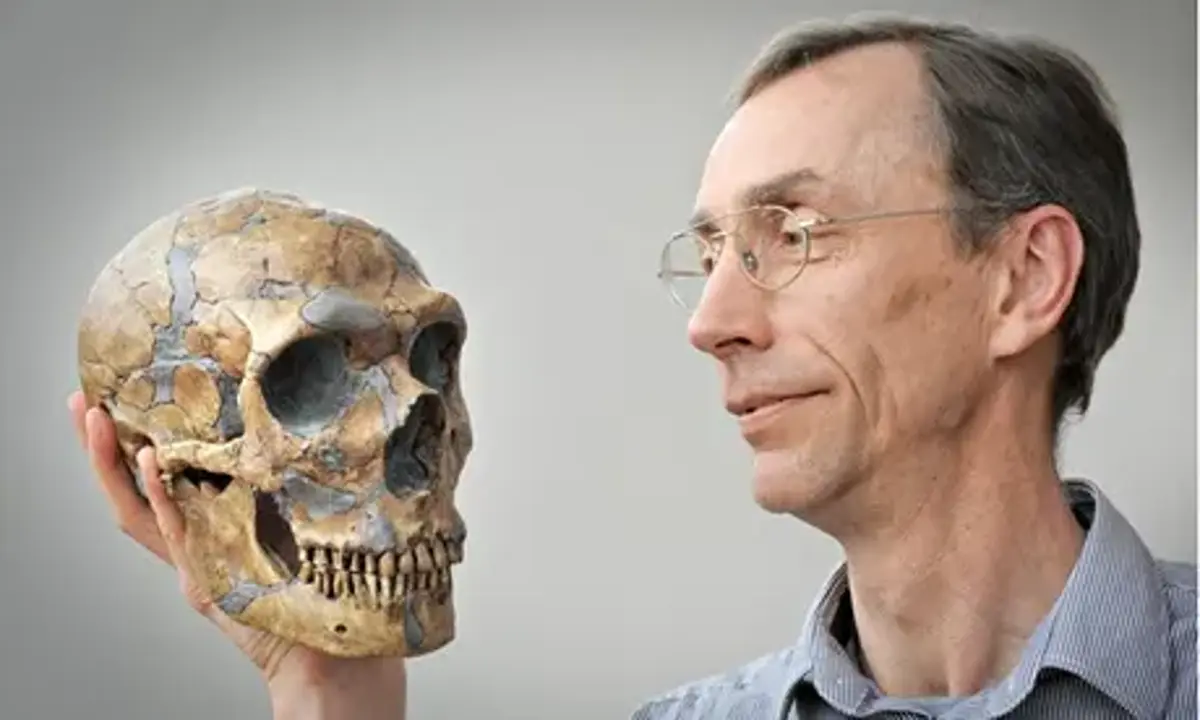
Pathbreaking discovery – Human Evolution and Paleogenomics
Genomics describes the sequences and analysis of an essential part of the nuclear genome of a given organism. Palaeogenomics is the study of ancient genomes, especially those of extinct organisms. In the field of palaeogenomics, Svante Pääbo has made stunning