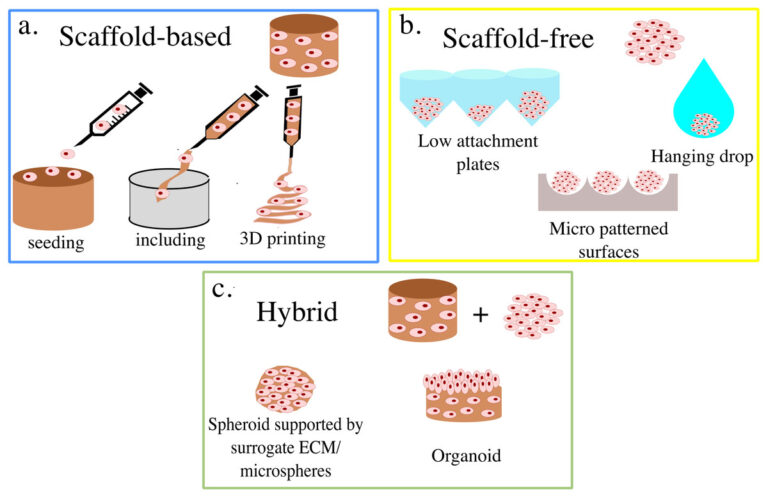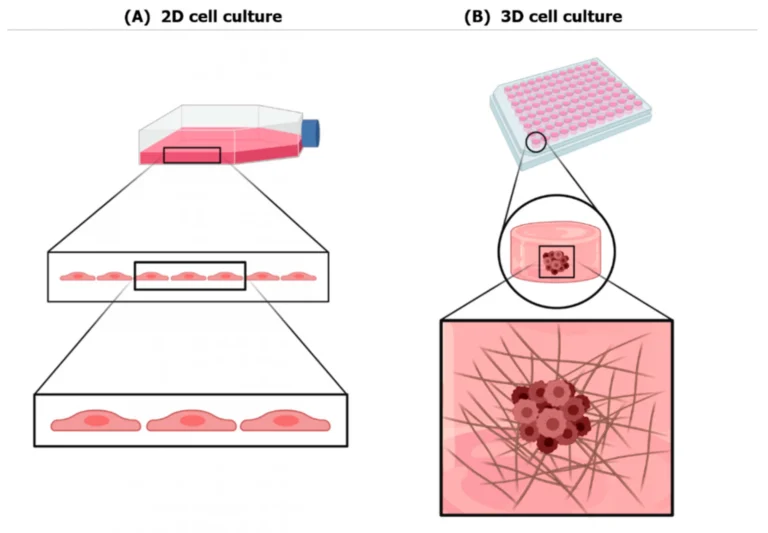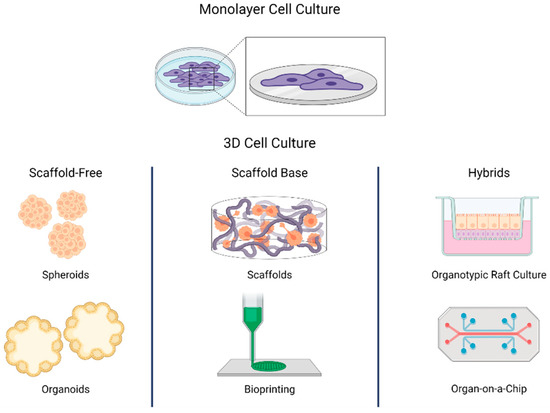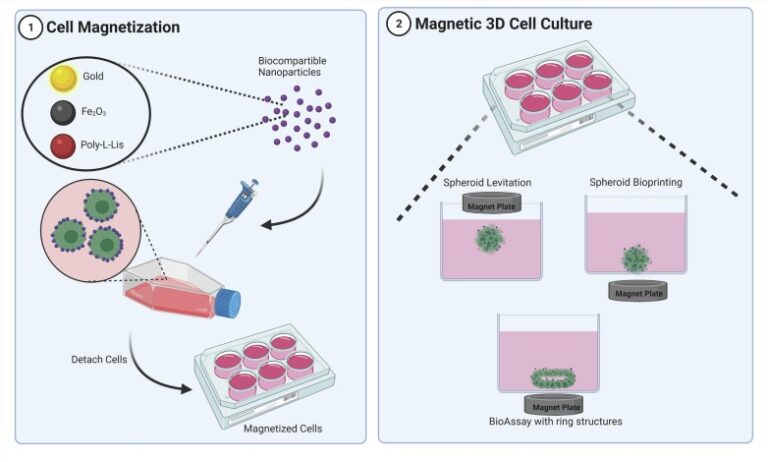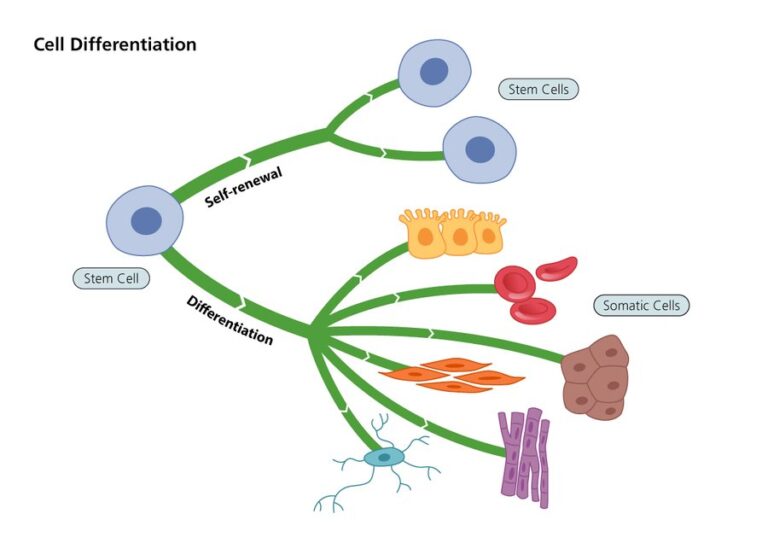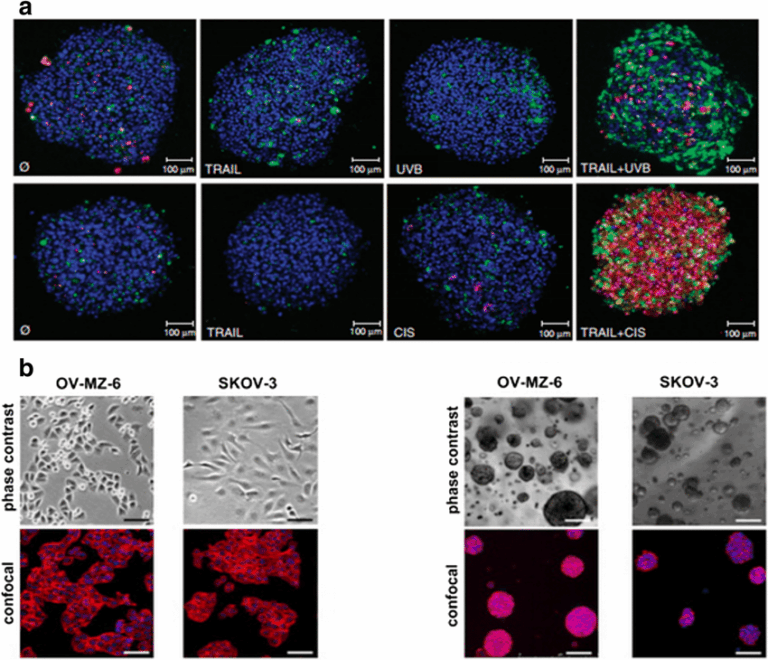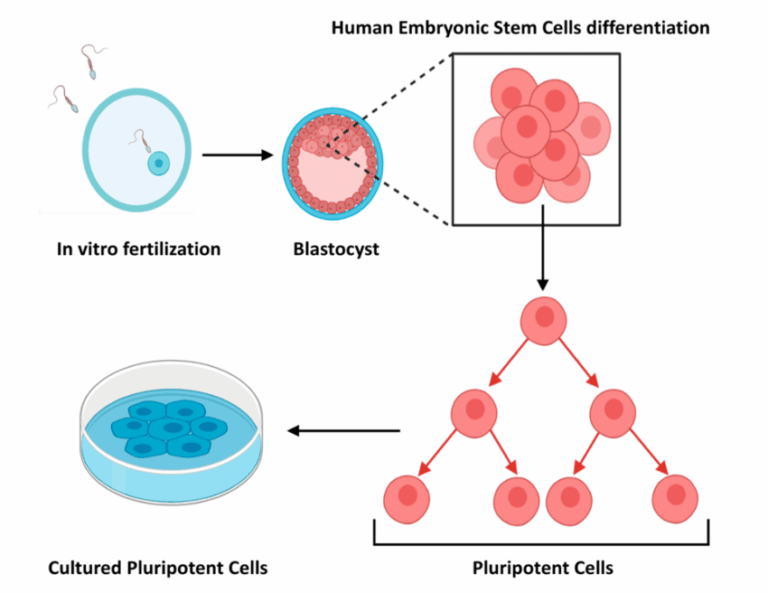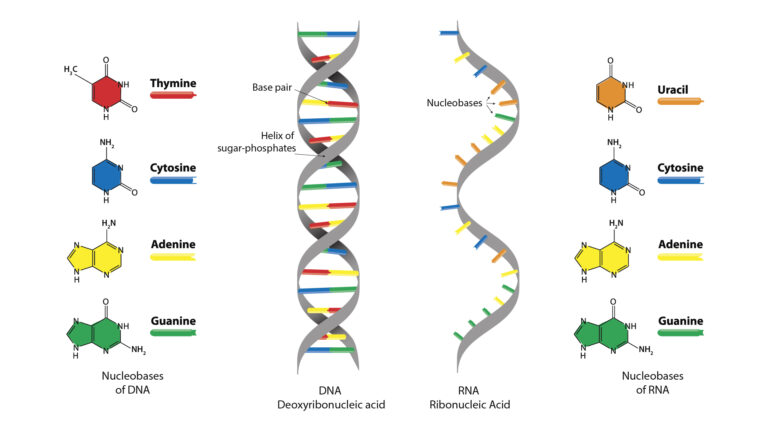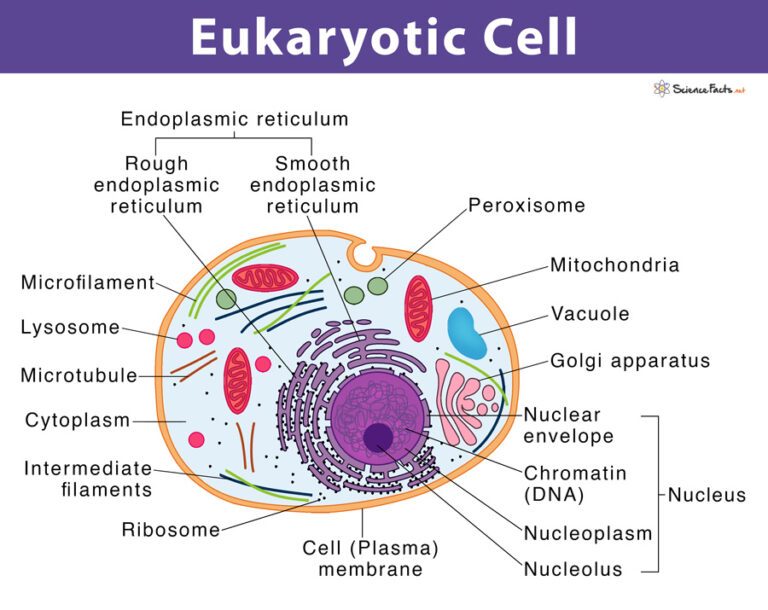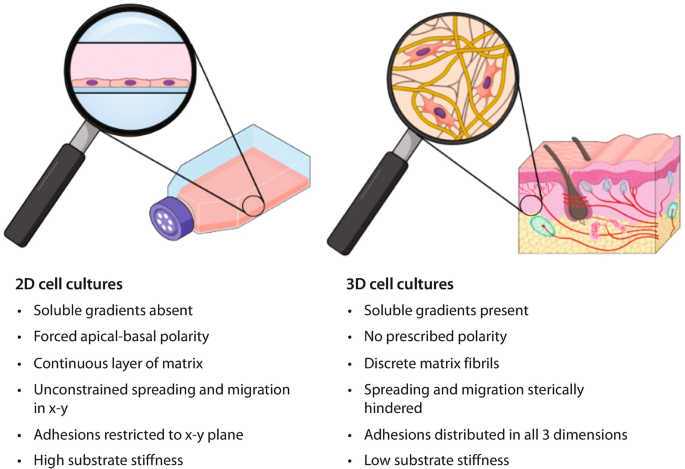
Is It The Right Time to Advance from 2D – 3D Cell Culture
Since the early 1900s, the two-dimensional (2D) cell culture method is used to culture cells and grow them in favorable artificial conditions (1) thereby playing a vital role in biomedical research (2). In line with…