The Shared Characteristics Of Spheroids And Tumors
Since its introduction, 3D cell culture has revolutionized cancer research by providing an efficient and modifiable research platform, that recapitulates in vivo like cell structure, function, gene expression and tissue microenvironment, all of which are important parameters for the drug
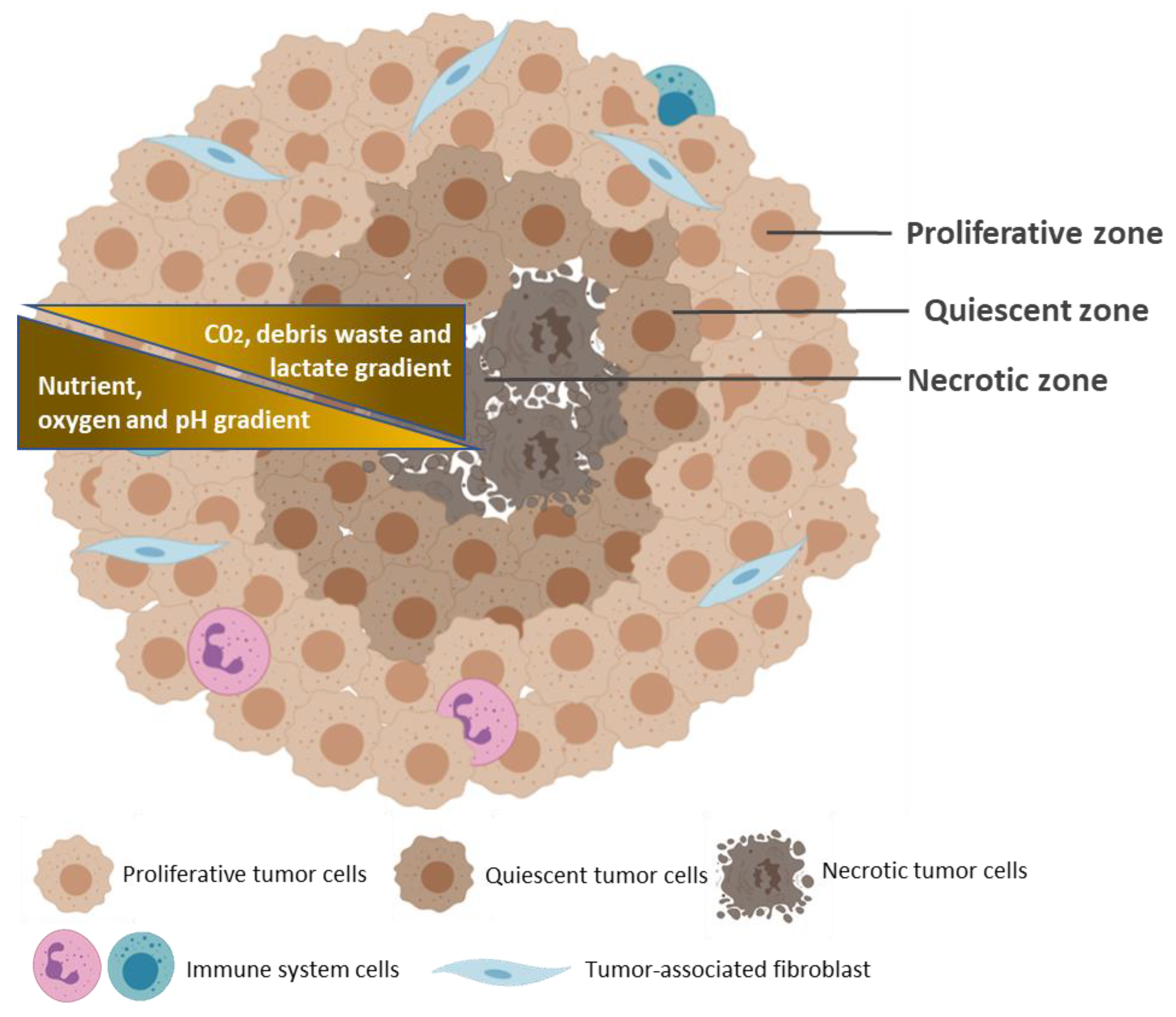
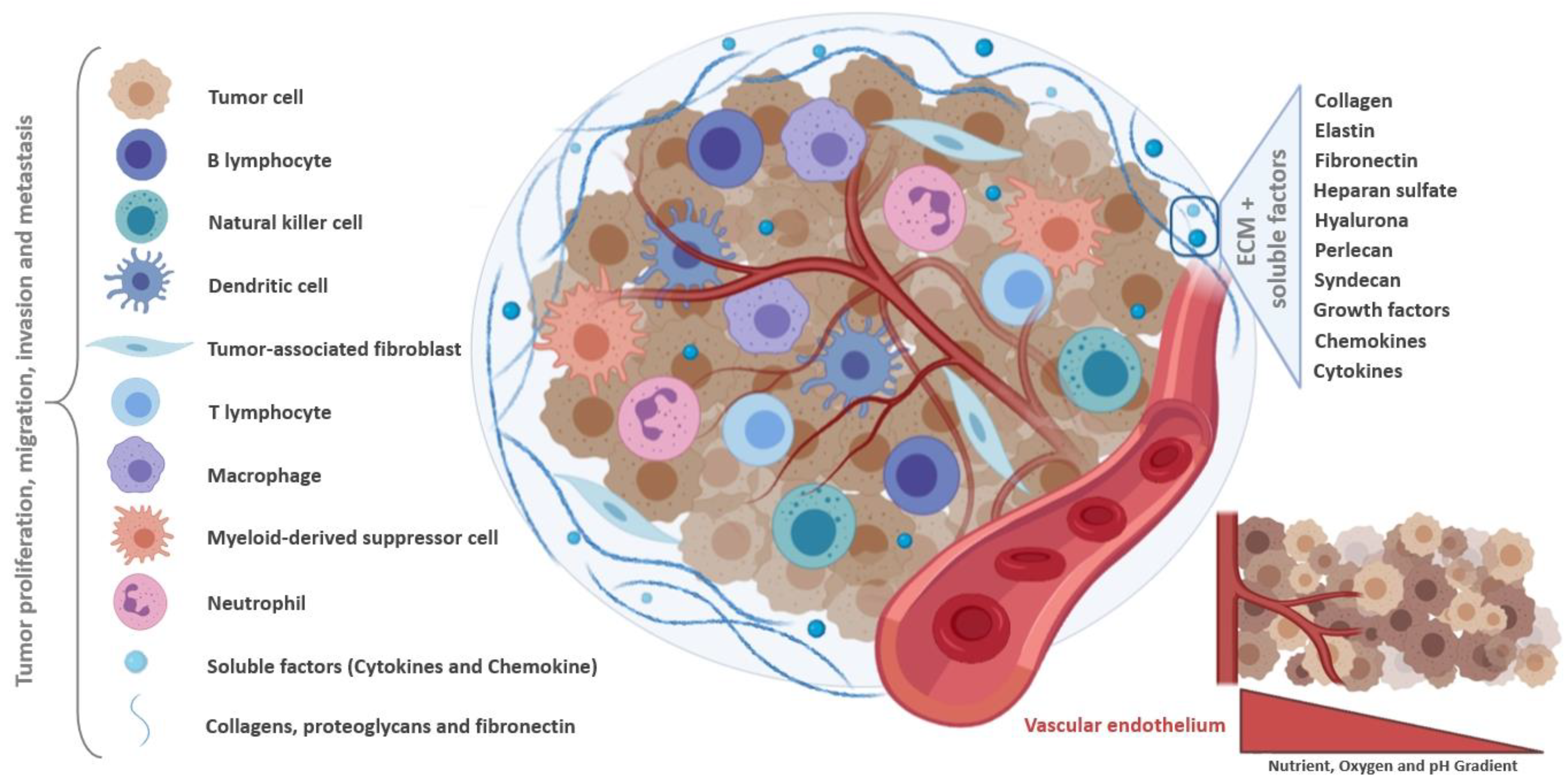
The Importance Of The Tumor Microenvironment In Cancer Research
Tumors derive from an abnormal growth of cells that occurs when cells continue to divide more than they should or when they do not enter programmed cell death. Tumors can be either benign or malignant. Malignant tumors are of most
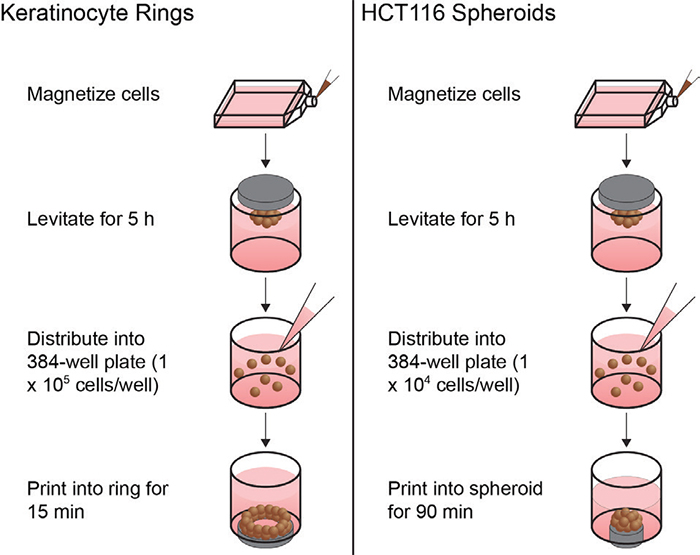
Magnetic 3D bioprinting: Principle, Applications, and Advantages
Three-dimensional (3D) cell culture models have gained more popularity over the last decade due to the advantages of better mimicking the in vivo microenvironment and tissue microarchitecture. However, applications of 3D cell culture models in high-throughput biomedical research are limited
Magnetic 3D bioprinting: Methods and Techniques
Magnetic 3D bioprinting uses magnetic fields to manipulate the positioning of magnetic nanoparticles or magnetized cells during the 3D printing process. The process of magnetic 3D bioprinting involves the following steps (1,2): 1. Preparing the magnetic particles or cells: Magnetic particles or
Organoid tumor models: benefits and challenges
Cancer is one of the most threatening diseases and leading cause of death worldwide (1). Intra- and intertumoral heterogeneity is often responsible for metastasis formation, treatment failure, and therapy resistance. The increase in the cost of research and development of
Types of three-dimensional cultures for drug screening
The rather low success rates in new drug development and the increased costs suggest that alternative and robust strategies are required to improve early drug discovery. Two-dimensional (2D) monolayer cultures do not provide a true in vitro representation of disease and
3D organ bioprinting with polymers : all you need to know
In the context of bioprinting, 3D printers use bioinks to print 3D organs which are prototypically similar to real organs. These 3D-printed organ-like structures have the potential to be used in vivo as organ transplants or in vitro in the
Stem cell Suspension Spheroid Cultures
Regenerative medicine largely depends on research performed using stem cells. Stem cells are characterized by stemness which is defined as the ability for self-renewal, to generate new stem cells from one original cell, and by multipotency, which refers to their
A comparison of 2D and 3D cell cultures
Cell culture is the process of growing cells outside of their natural environment, typically in a laboratory setting. It involves the cultivation of cells in a controlled environment, usually in a special liquid medium that provides the necessary nutrients and