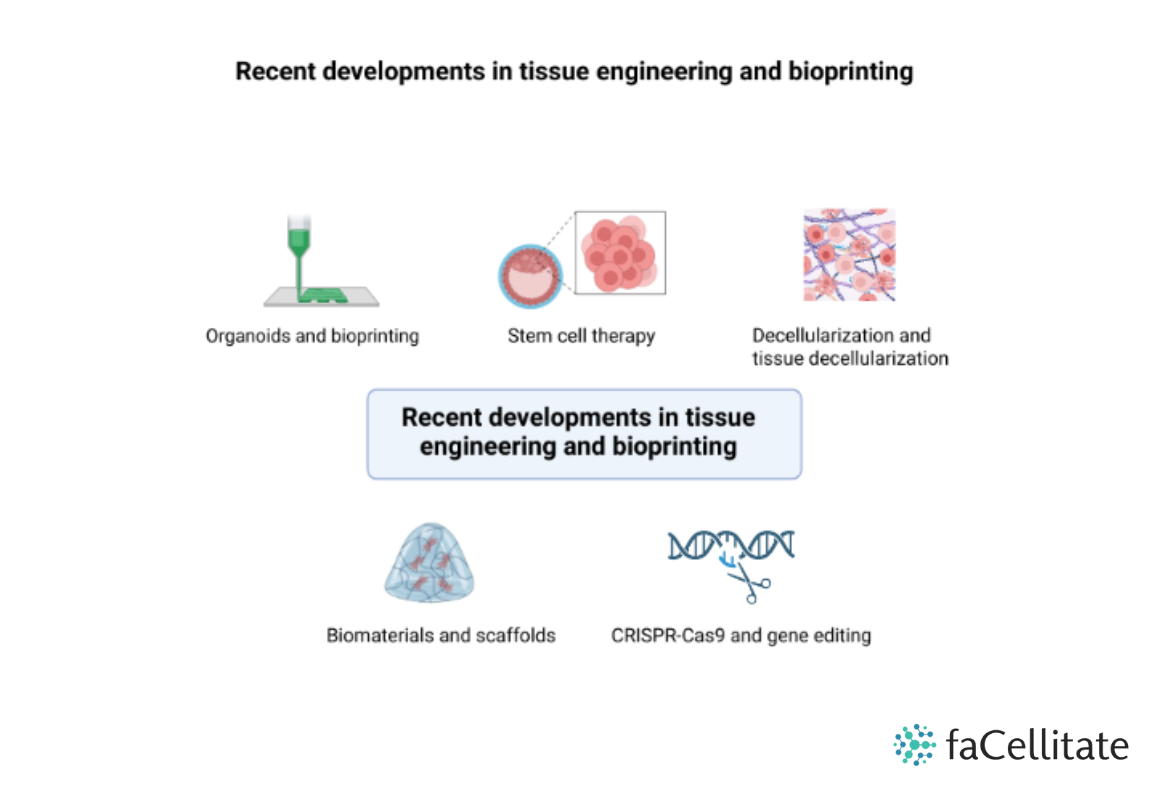
Recent developments in tissue engineering and bioprinting
Organoids and bioprinting
Researchers have been able to create miniature, simplified versions of organs called organoids for various tissues, such as the liver, kidney, brain, and gut, providing valuable tools for studying organ development, disease modeling, and drug testing. Bioprinting uses 3D printing technology to create tissue-like structures and has also seen significant progress in terms of accuracy and complexity, offering the potential for personalized tissue replacement and regeneration.
Stem cell therapy
Stem cells, with their ability to differentiate into various cell types, have shown great promise in tissue engineering. Advances have been made in the isolation, expansion, and differentiation of stem cells for specific tissue repair and regeneration purposes.
Biomaterials and scaffolds
Biomaterials play a crucial role in tissue engineering by providing a supportive environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration. These materials can act as scaffolds to support cell attachment, migration, and proliferation while promoting tissue regeneration.
Decellularization and tissue decellularization
Decellularization involves removing cellular components from tissues or organs while preserving the extracellular matrix. The resulting “scaffolds” can then be repopulated with new cells, either from the same individual (autologous) or a different donor (allogeneic), to create functional tissues for transplantation.
CRISPR-Cas9 and gene editing
The revolutionary gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9 has opened up new possibilities in tissue engineering. Researchers have been exploring its potential for correcting genetic mutations that cause certain diseases, as well as for enhancing the regenerative potential of cells used in tissue engineering.
Vascularization
Recent efforts have focused on developing methods to induce vascularization within the tissue constructs, as creating a vascular network to supply the engineered tissue with nutrients and oxygen is an ongoing challenge.
References
1. Dzobo K, Thomford NE, Senthebane DA, Shipanga H, Rowe A, Dandara C, Pillay M, Motaung KSCM. Advances in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: Innovation and Transformation of Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 30;2018:2495848. doi: 10.1155/2018/2495848. PMID: 30154861; PMCID: PMC6091336.
2. Pearson RG, Bhandari R, Quirk RA, Shakesheff KM. Recent Advances in Tissue Engineering. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2017;27(2-4):199-231. doi: 10.1615/JLongTermEffMedImplants.v27.i2-4.70. PMID: 29773040.
3. Sharma P, Kumar P, Sharma R, Bhatt VD, Dhot PS. Tissue Engineering; Current Status & Futuristic Scope. J Med Life. 2019 Jul-Sep;12(3):225-229. doi: 10.25122/jml-2019-0032. PMID: 31666821; PMCID: PMC6814873.