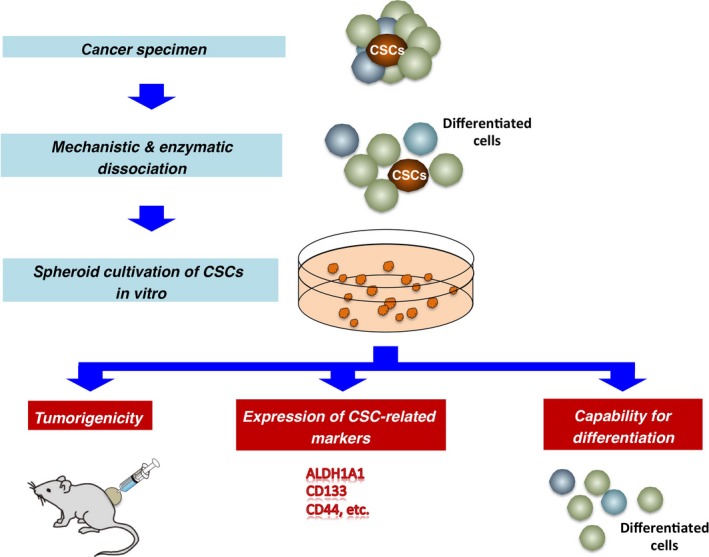
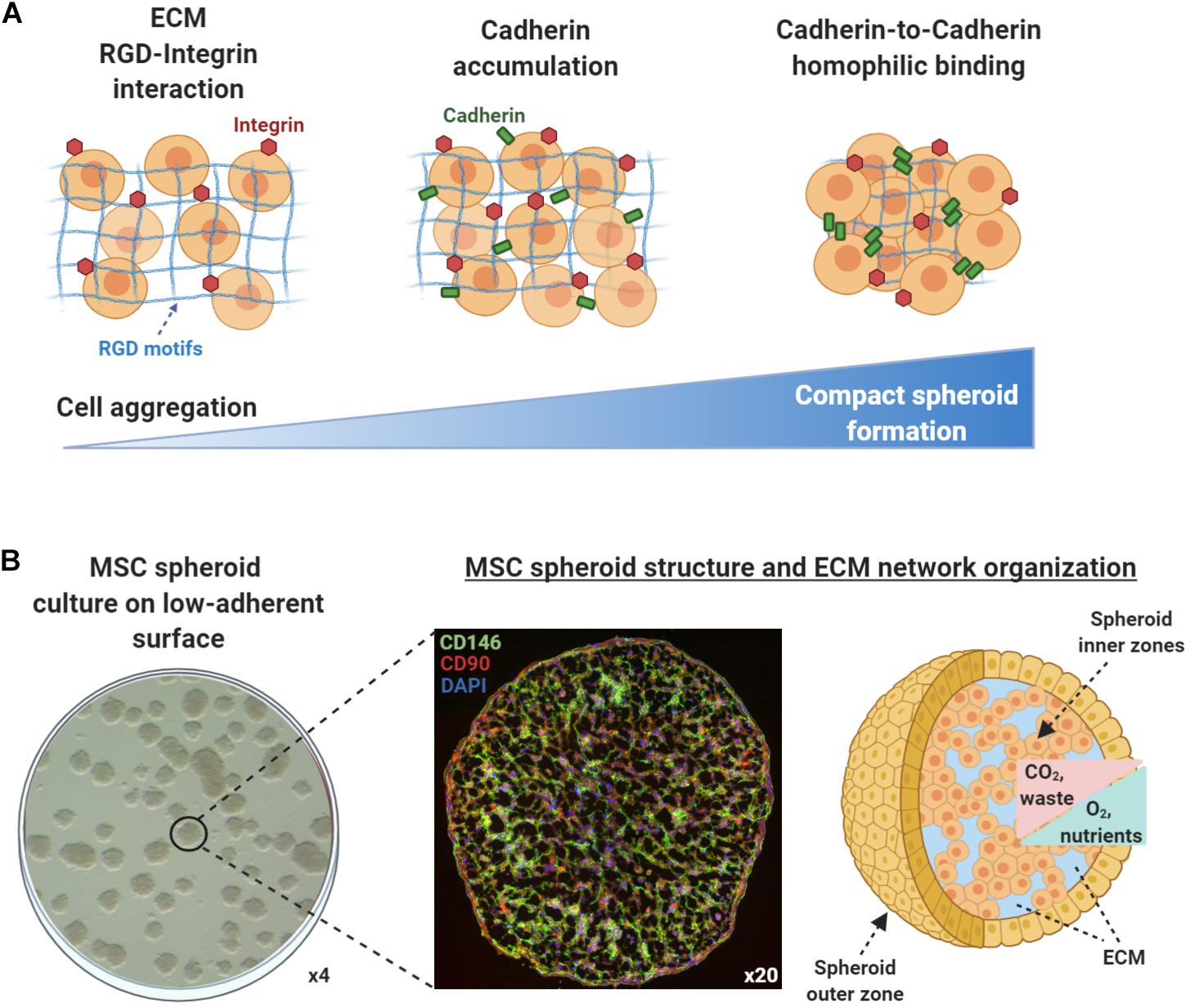
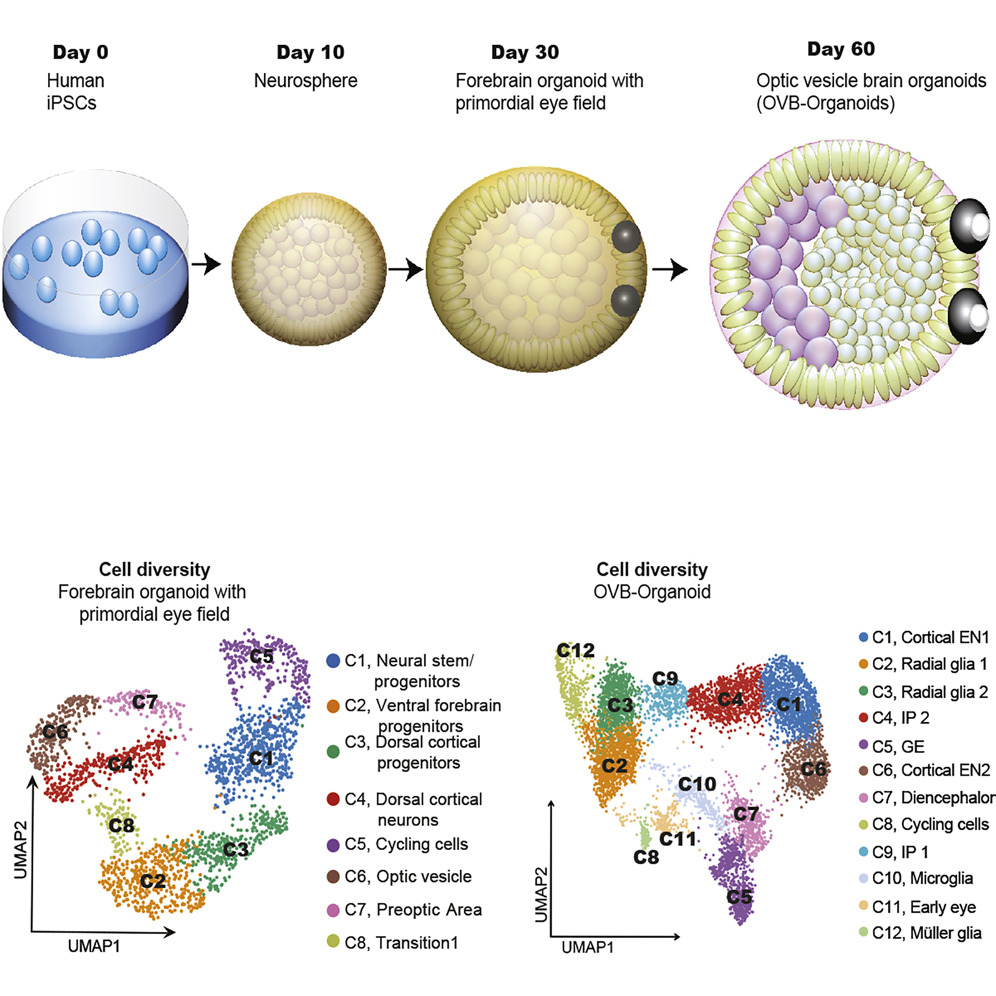
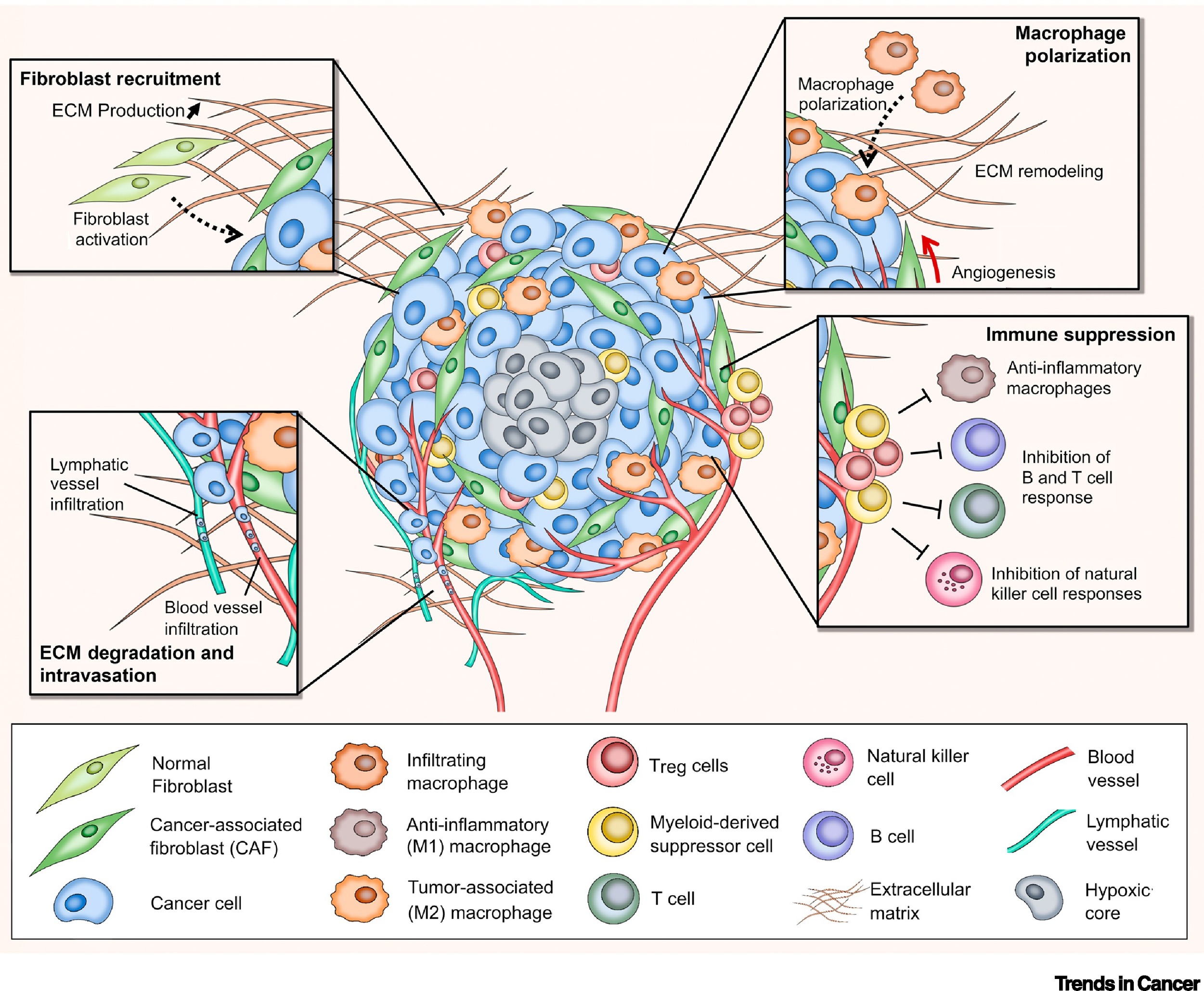
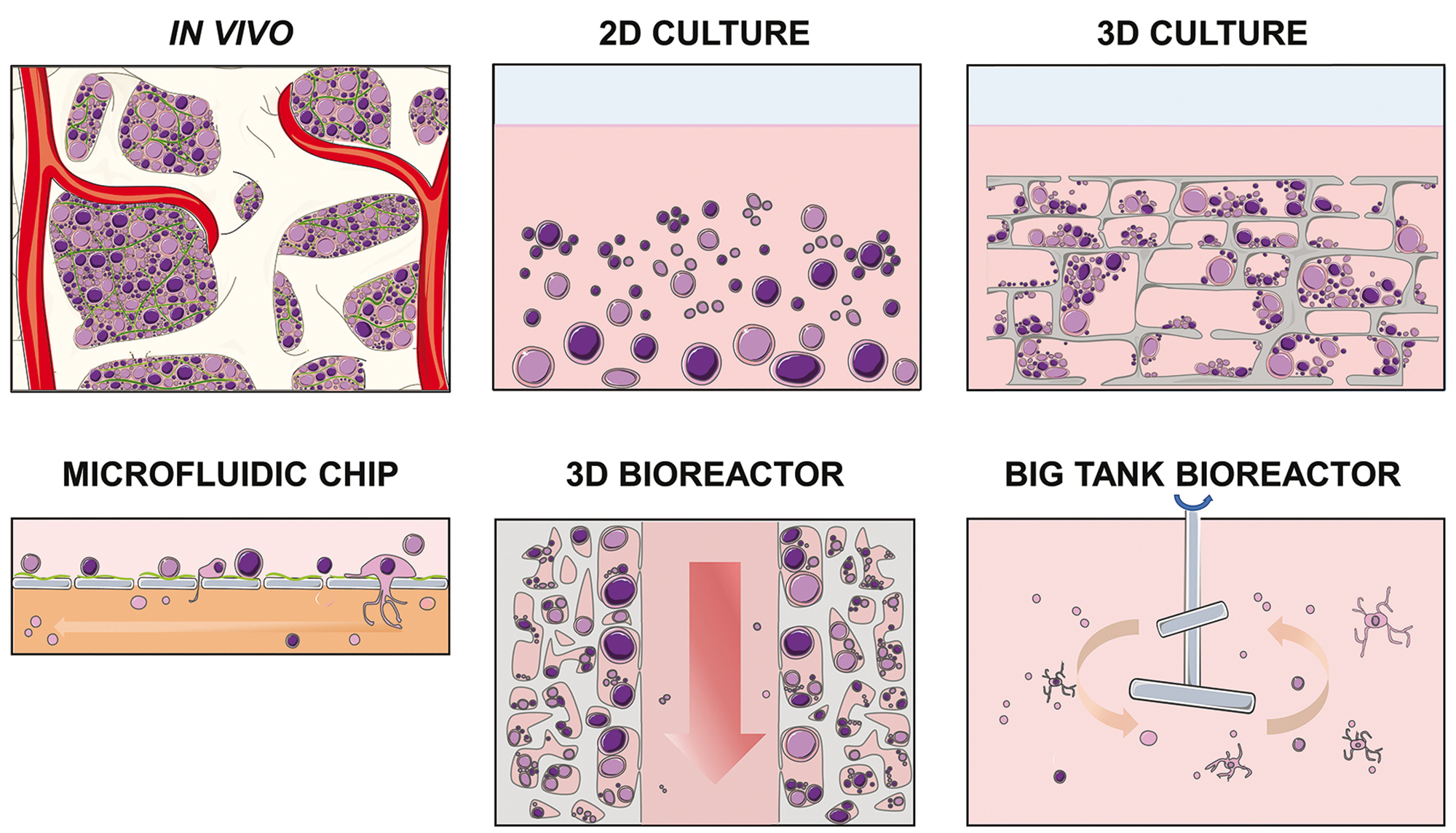
3D models of cancer cells
Tumor cells typically grow in 3-dimentional configurations. The surrounding tumor microenvironment is composed of non-tumor cells, and extracellular matrix (ECM). Within this microenvironment, tumor cells face hard growth conditions that include low oxygen exposure and nutrient levels and a susceptible
Stem cell spheroids – A vital tool in regenerative medicine
Stem cells serve as the primary resource in regenerative medicine including tissue engineering and transplantation therapy. To this effect human mesenchymal stem cells contain secretory factors with anti-inflammatory, angiogenic and immune regulation factors that makes them an efficient resource for
ORGANOIDS: CONSTRUCTS DERVIED FROM STEM CELLS
Organoids can be defined as three-dimensional multicellular in vitro tissue culture that has the capability to mimic its corresponding in vivo organ, so that they can be put in use to study characteristics of that organ in the tissue culture
3D Spheroid culture of Stroma cells
Three-dimensional (3D) cultures are widely accepted as an excellent in-vitro model of high through out drug screening, preclinical cancer research and cancer/stem cell research. 3D spheroid models are morphologically and functionally representative of in-vivo cell state, and are able to
Blood cells in 3D cell culture
In recent decades there has been a strong move from 2 dimensional cell cultures to 3D cell culture systems as a laboratory tool to recapitulate the morphology of native human tissues. 3D cell culture systems has been quite challenging to
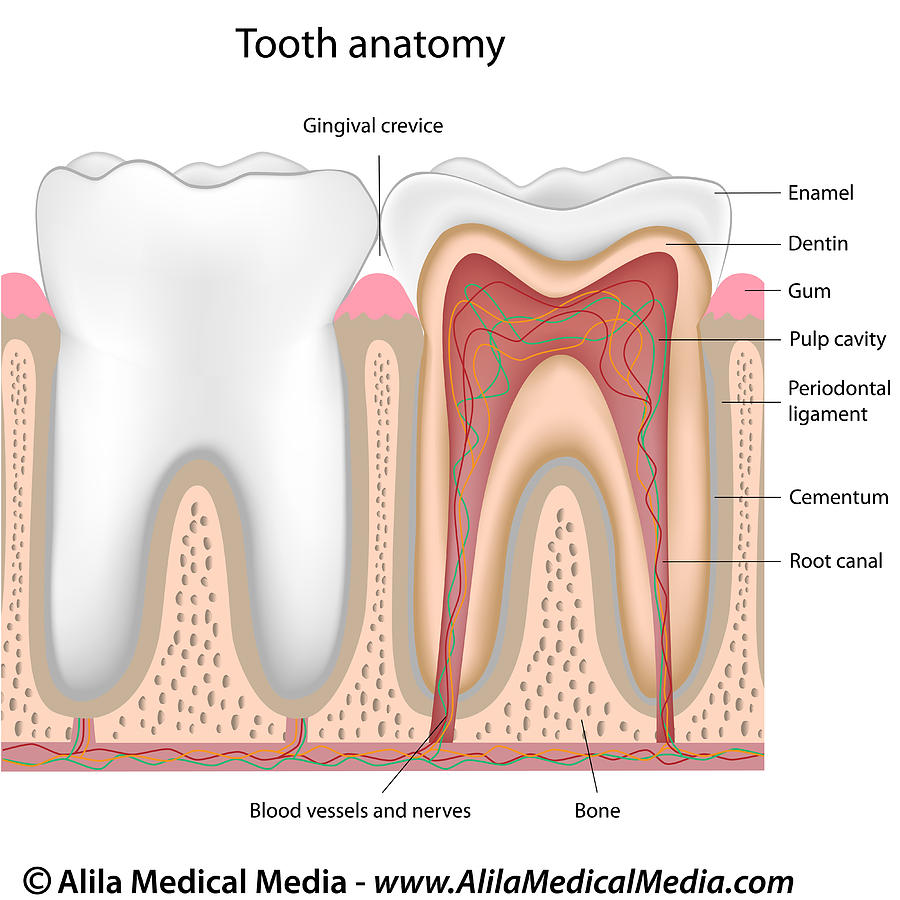
Dental cells
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) are derived from the dental pulp; the soft living tissue within teeth. These cells are pluripotent and are able to differentiate into tissues that bare similarity to mesoderm, endoderm and ectoderm layers (Atari et al,
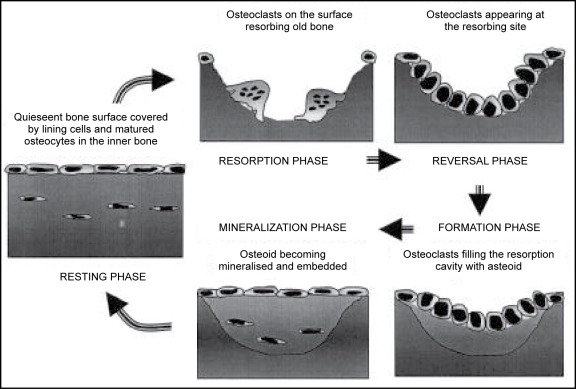
Bone microenvironment
Bone is a mineralized connective tissue composed of four types of cells namely, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and bone lining cells. Bone tissue is constantly undergoing remodeling via the bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts. Osteocytes operate as
The Pancreatic islets
The pancreas is both an exocrine and an endocrine gland. The exocrine functions are performed by acinar cells, which secrete digestive enzymes. The endocrine role is played by the pancreatic islets; group of cells comprising of alpha, beta, delta and
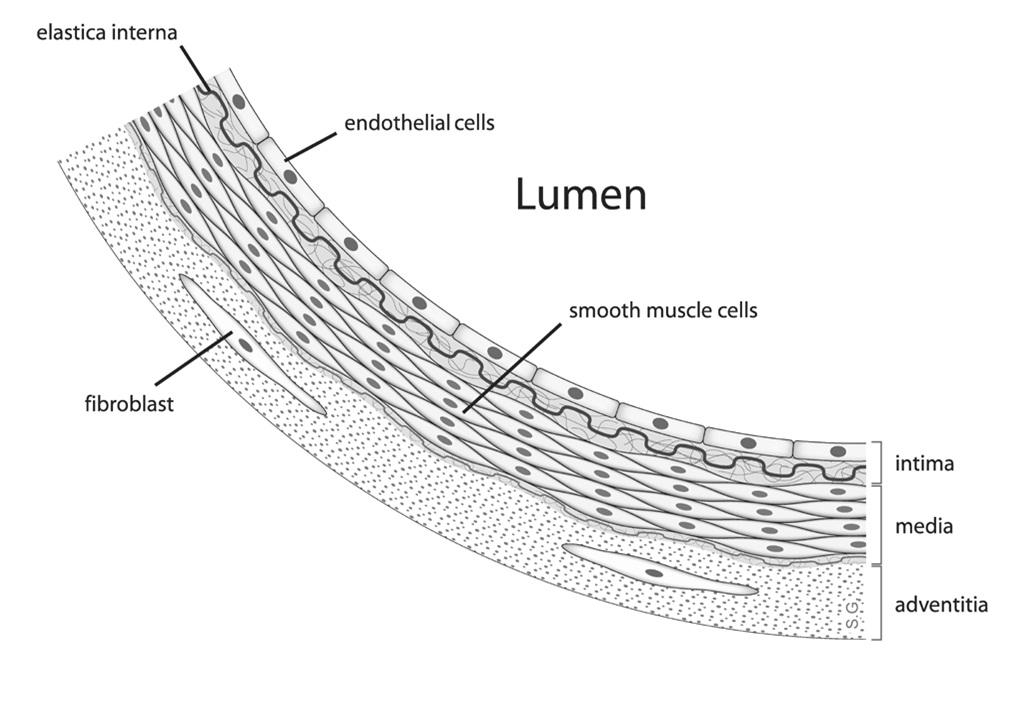
The Endothelium: An interface between Blood, tissue and lymph
The Endothelium consists of a single layer of squamous endothelial cells, forming the inner lining of the circulatory system. It is has varying degrees of permeability depending on the organ physiology as it operates as a barrier between vessels and
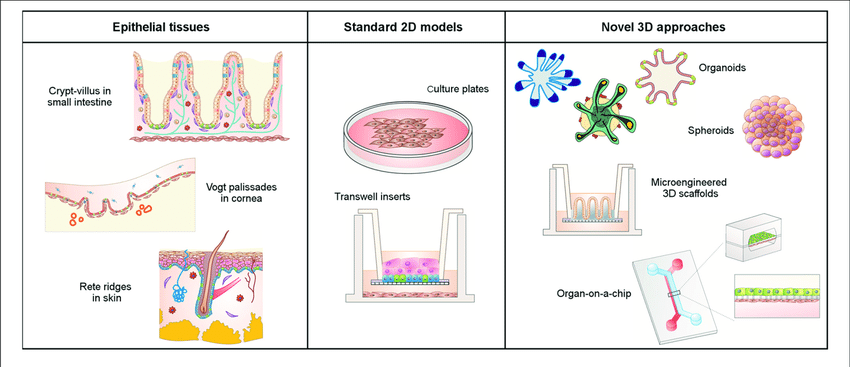
Epithalial cells for spheroid formation
The Epithelium is a thin, continuous, layer of tightly packed cells formed as complex 3D structures such as cysts, tubules or invaginations. The shape of the epithelium is essential for its function as it aids in creating biochemical gradients that