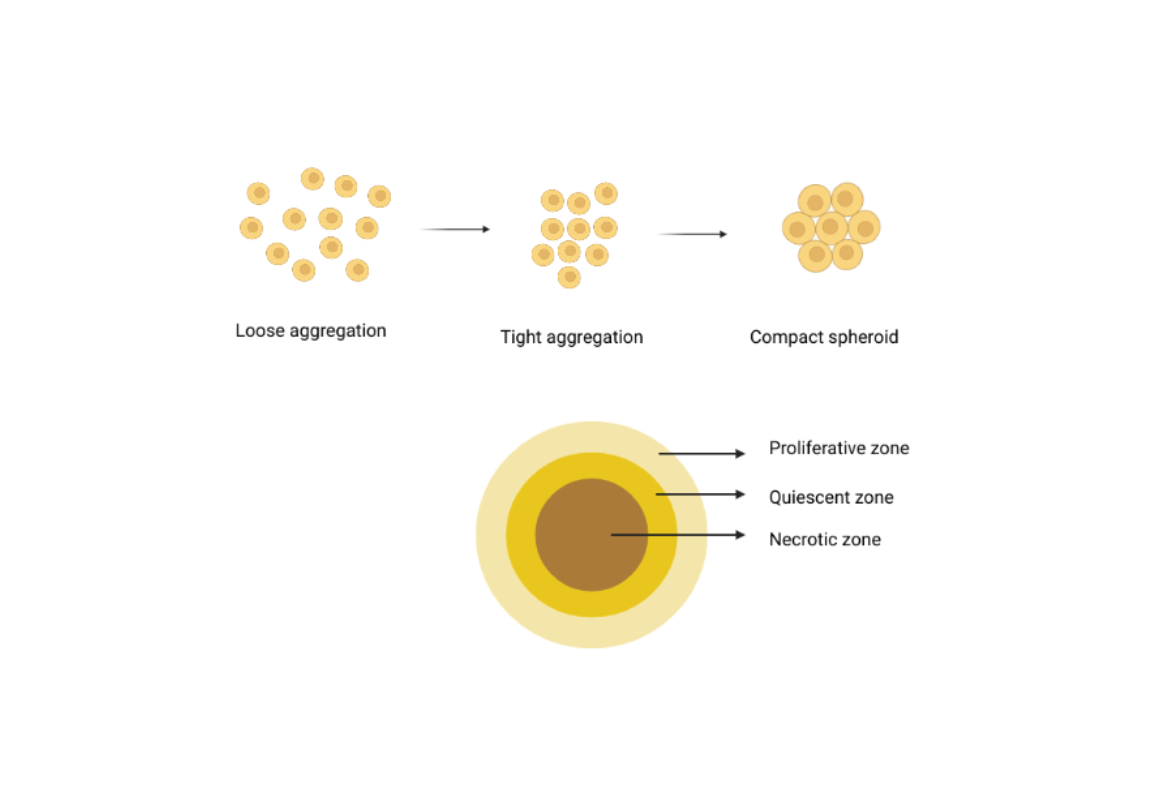
Necrosis and its formation in a spheroid
The term necrosis refers to cell or tissue death and is typically caused by factors such as injury, infection, or inadequate blood supply. Necrosis can also form within a spheroid, which is a 3D culture of cells. Here are a few
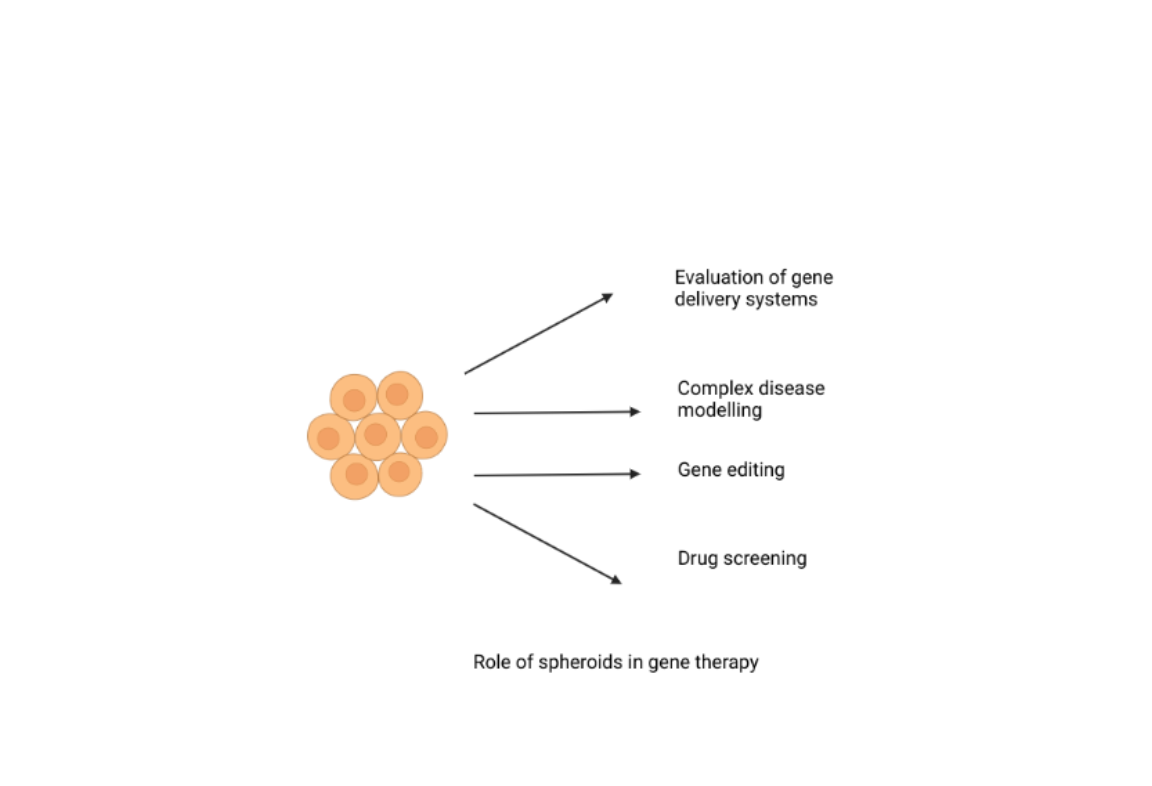
The role of spheroids in gene therapy
Spheroids are multicellular cell aggregates that self-assemble in 3D structures when cultivated in an environment that prevents attachment to the artificial surface, such as BIOFLOAT 96-well plates with their anti-adhesive properties. Spheroids can be generated from a wide range of cell
Factors affecting tumor spheroid formation for cancer research
Tumor spheroids are three-dimensional cell culture models that have gained significant attention in cancer research because they provide a more physiologically relevant environment for studying tumor biology compared to traditional two-dimensional cell culture systems. 3D spheroids contain a dense network of
Non-Adhesive Well Plates For Spheroid Generation
Spheroid are defined as 3-dimentional cell aggregates that are formed via spontaneous self-assembly of cells when cultivated on a cell repellant, non-adhesive surface. Spheroids are by far one of the most popular scaffold-free 3D cell culture methods, and are low
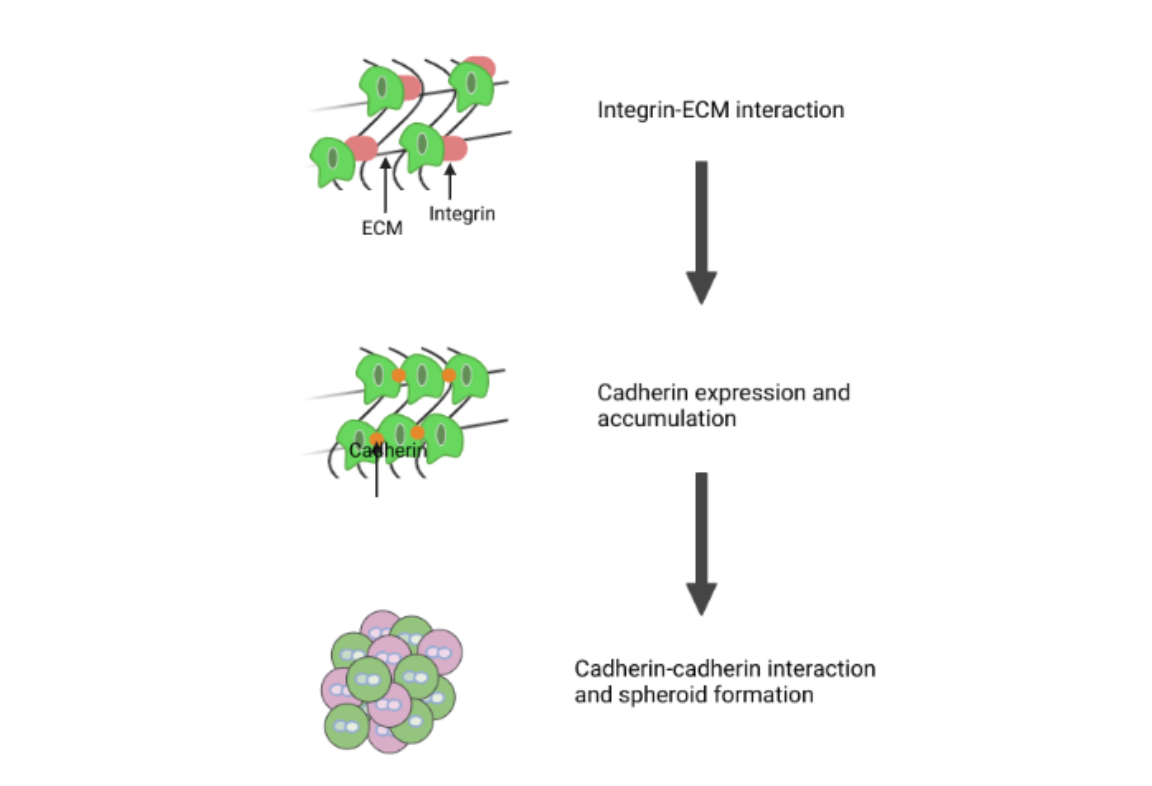
Spheroid formation: Mechanism and role of the substrate
Spheroids grow in three dimensions to form a sphere-like structure which mimics cell in vivo microenvironment more closely than conventional 2D monolayer cell culture. They can be formed from single or multiple cell types that are commonly used in research
Challenges in spheroid research
Spheroids have gained significant popularity in cancer research because of their more physiological relevance for studying tumor biology compared to traditional two-dimensional cell culture systems. However, several issues are associated with using multicellular spheroids in cancer research. This article is an
Spotlight on the applications of precision medicine
Modern medicine and therapies are designed to treat large groups of people with the same disease. Doctors may consider the sex, age, or medical history of the patient but most of the treatments are still based on what is most
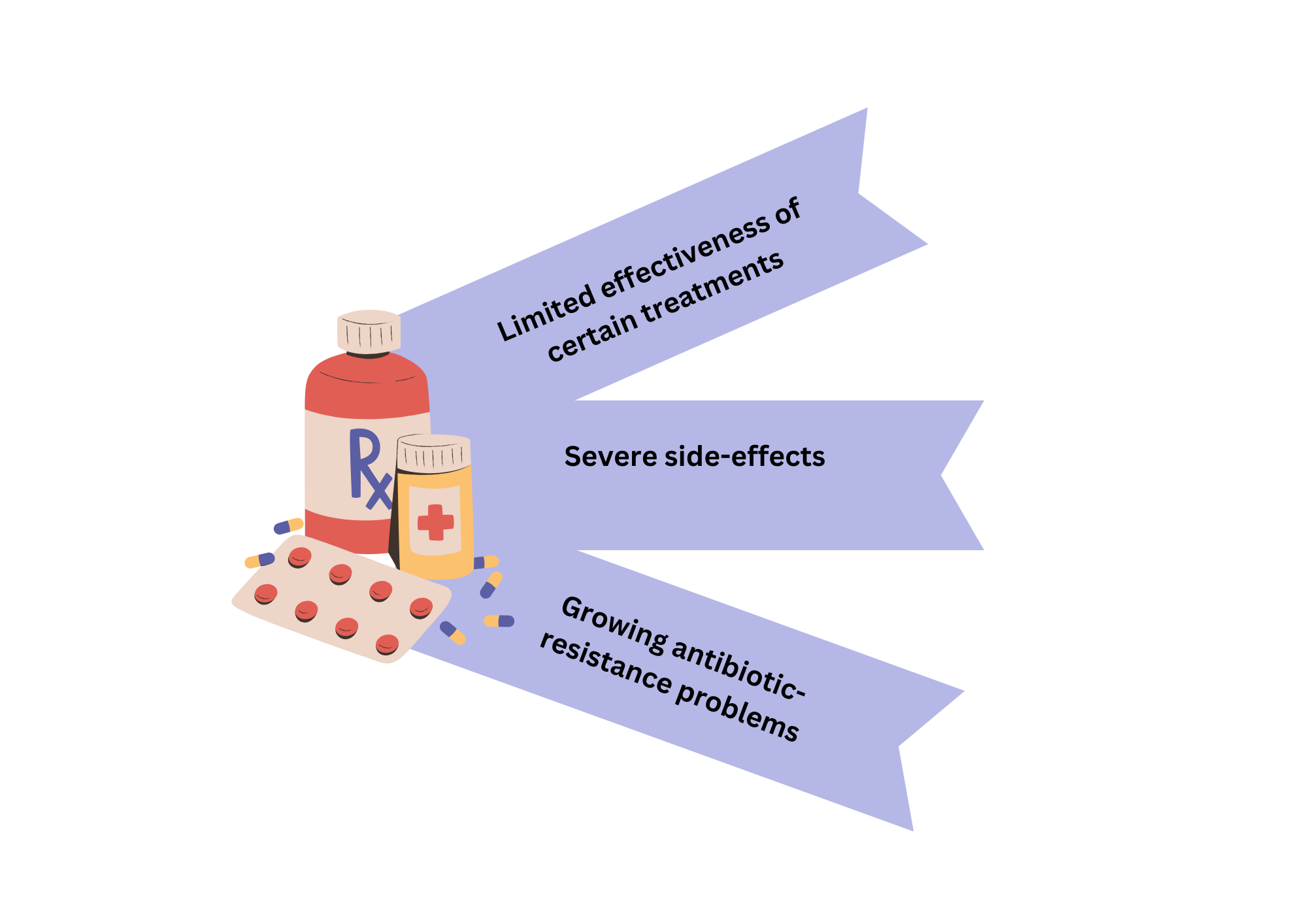
An overview of the limitations of modern medicine
Modern medicine involves drugs, surgeries, and medical practices that are currently used to diagnose, treat, and prevent illnesses and diseases. The combination of science, research, and technology has enabled significant advancements in the field of healthcare (1). While modern medicine
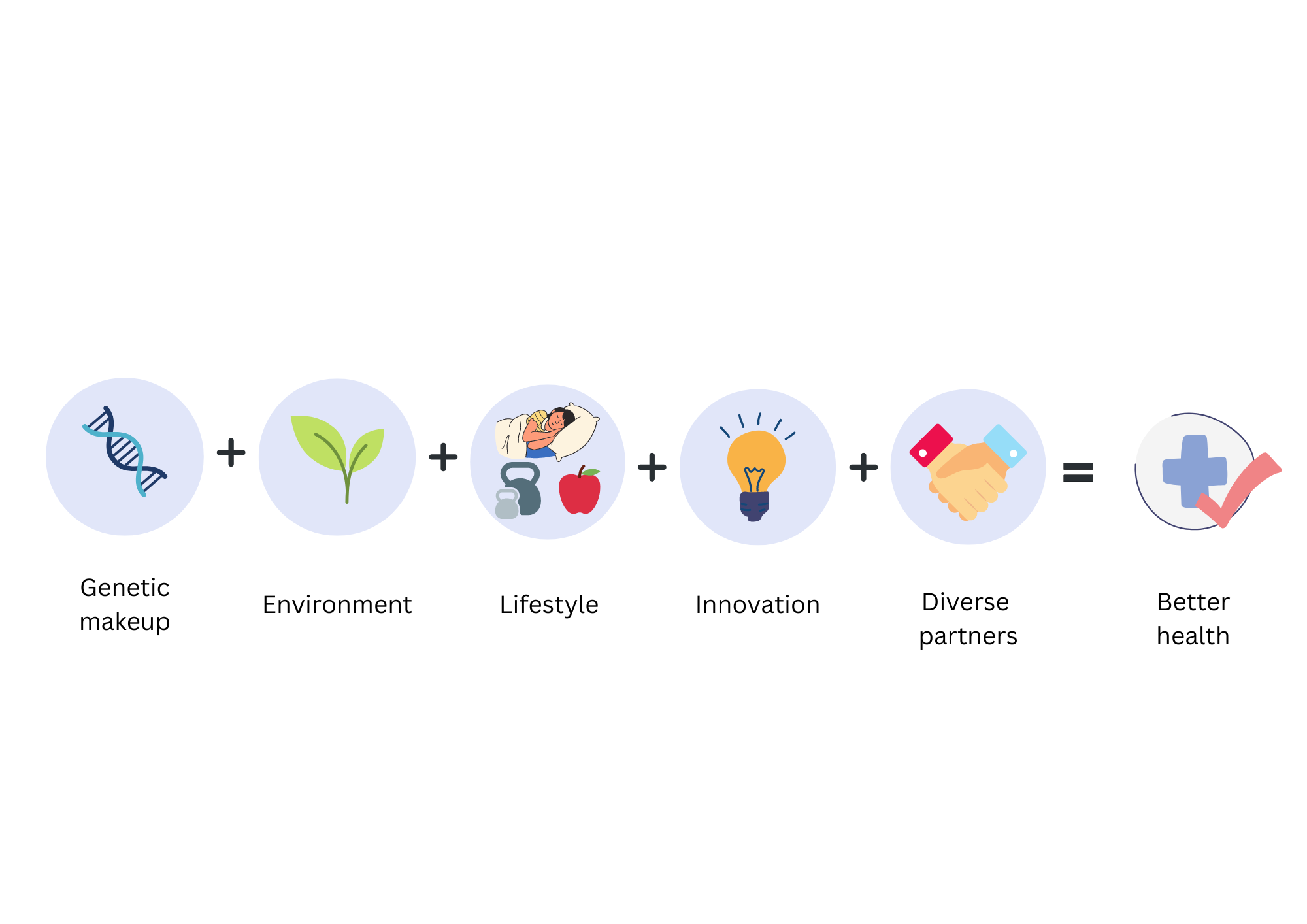
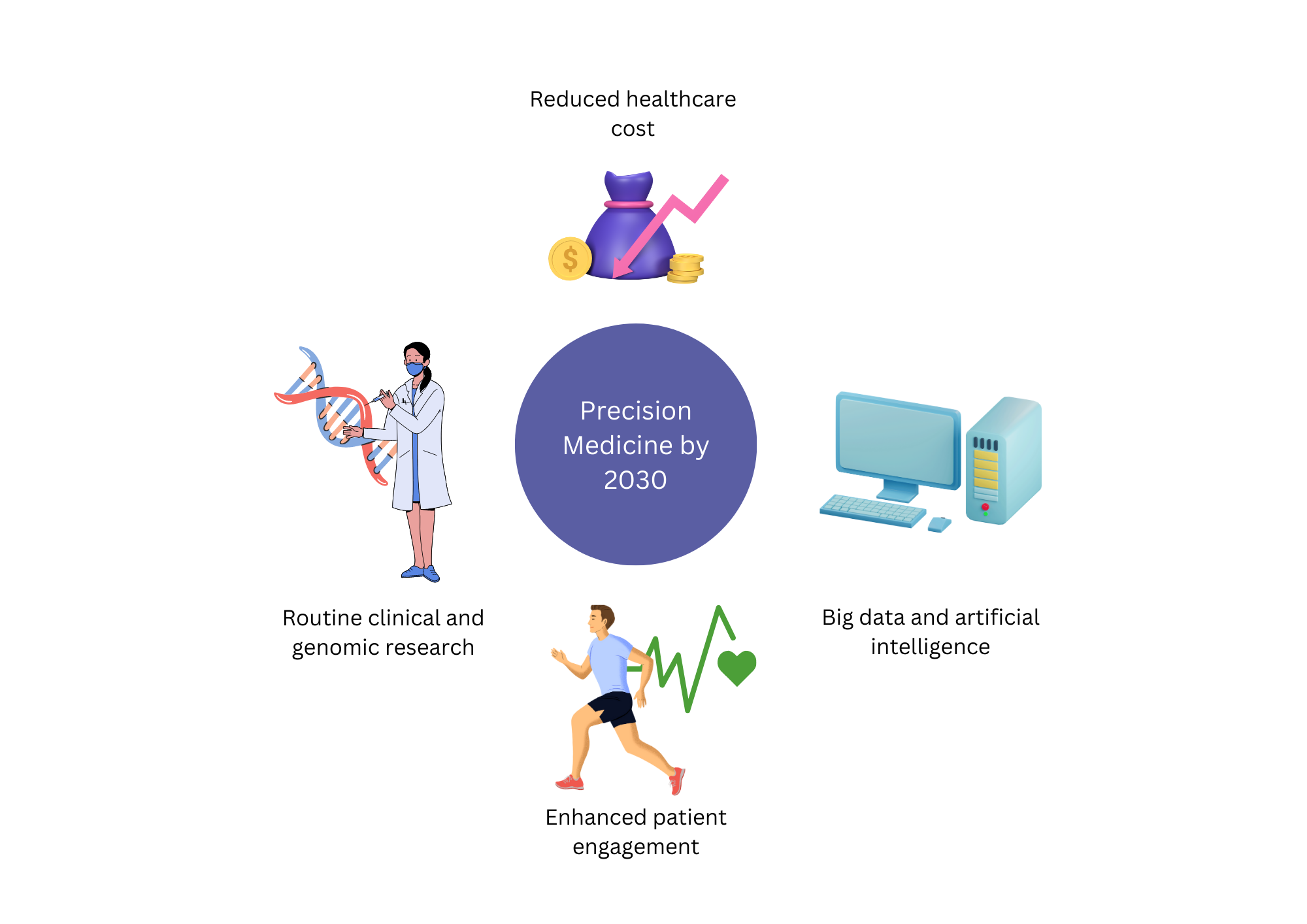
How is precision medicine poised to transform healthcare by 2030
The field of precision medicine is rapidly evolving to tailor therapies and treatments based on an individual’s unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle data. It has the potential to transform healthcare by improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. Thanks to advances
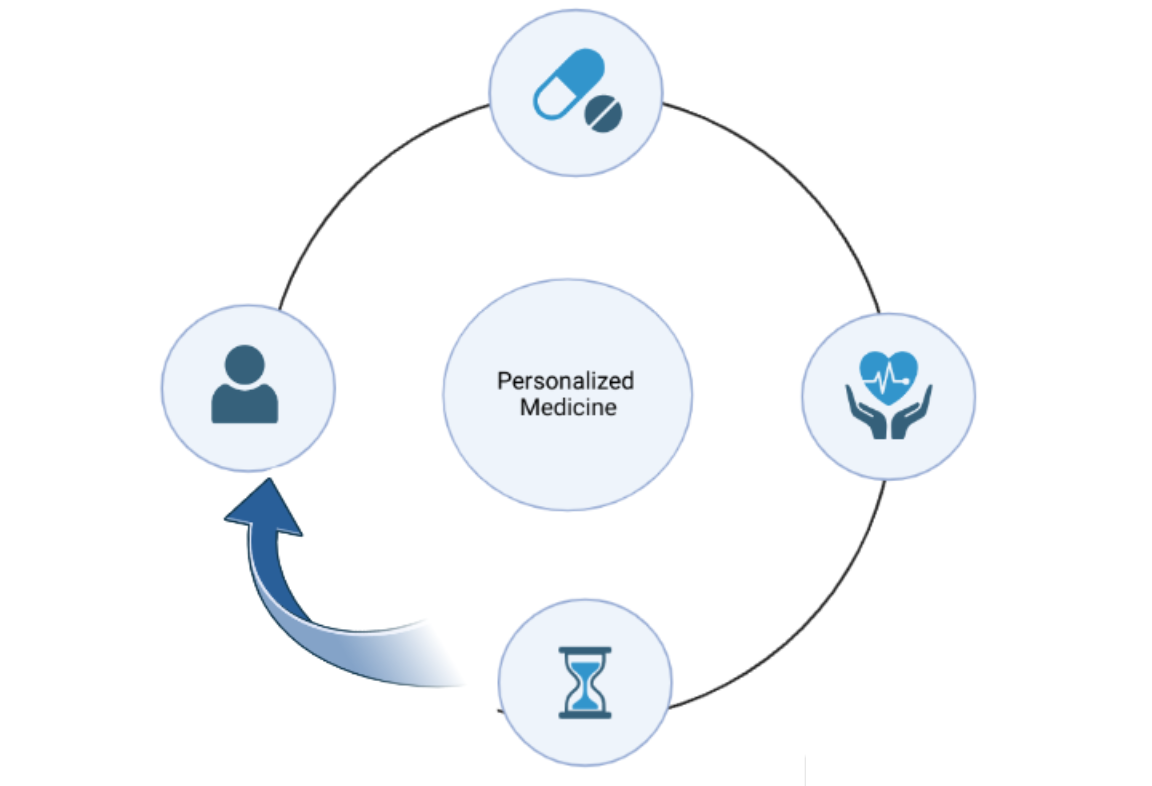
Introduction to precision medicine and its key benefits
Precision medicine is a healthcare approach to treat diseases and illnesses considering individual differences in genes, lifestyle, and environment. It involves tailoring medical decisions, interventions, and therapies to patients’ unique characteristics, allowing more accurate and effective treatment (1). Precision medicine involves