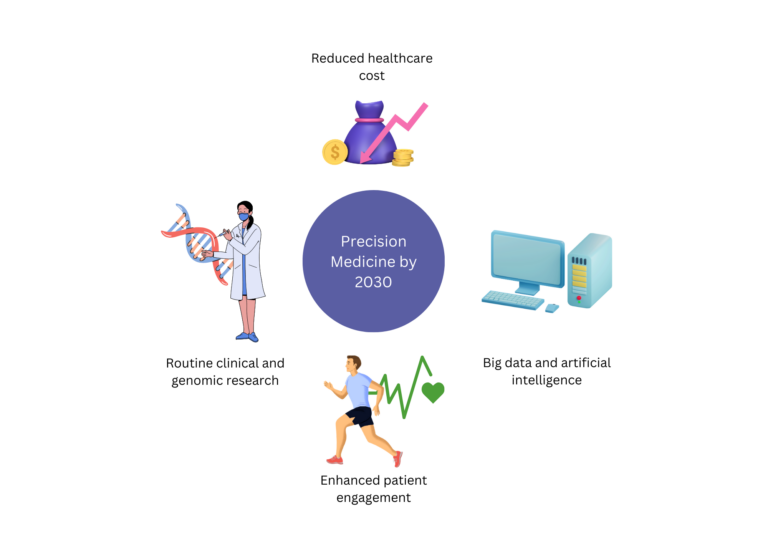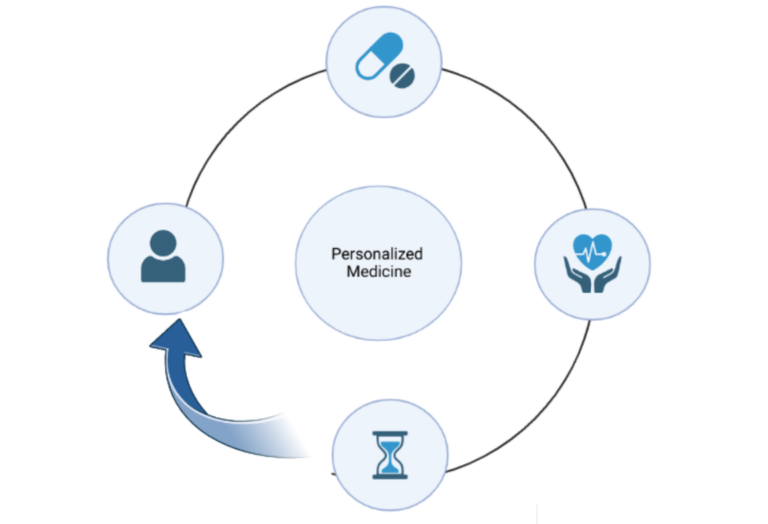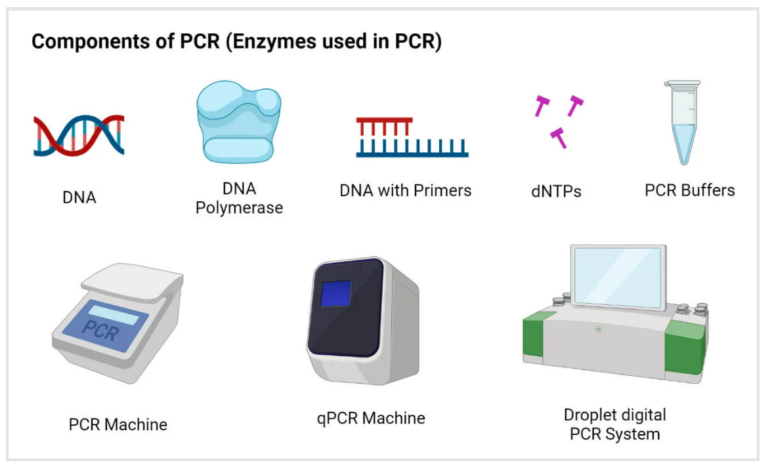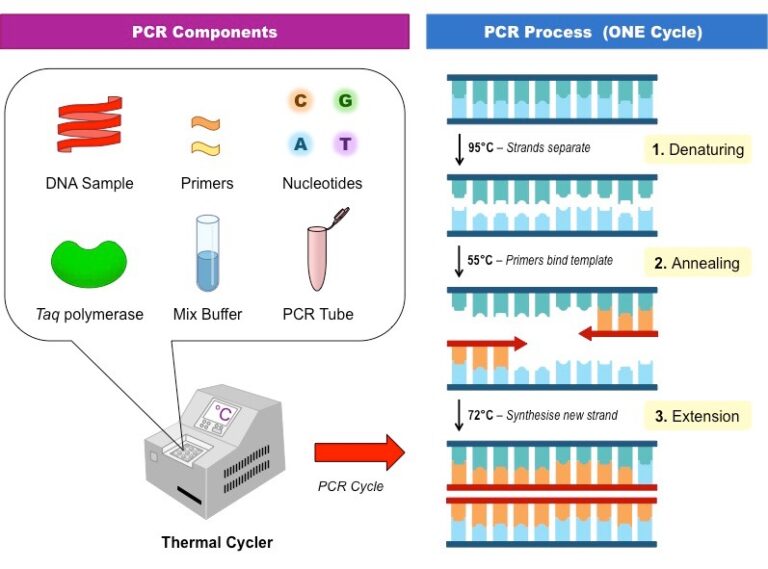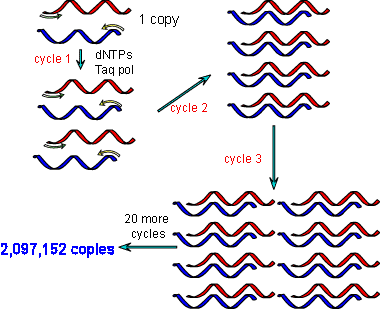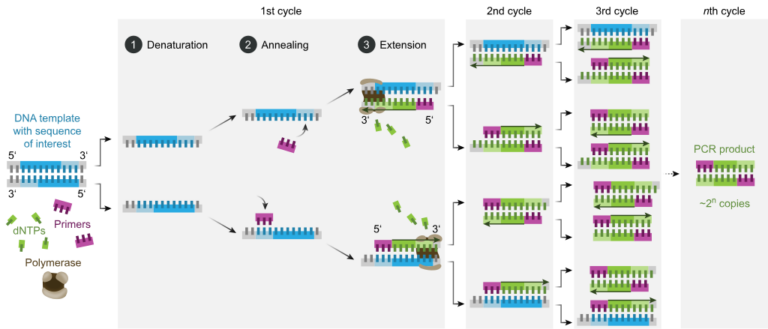
An overview of the limitations of modern medicine
Modern medicine involves drugs, surgeries, and medical practices that are currently used to diagnose, treat, and prevent illnesses and diseases. The combination of science, research, and technology has enabled significant advancements in the field of…