What are primary cells : advantages and limitations
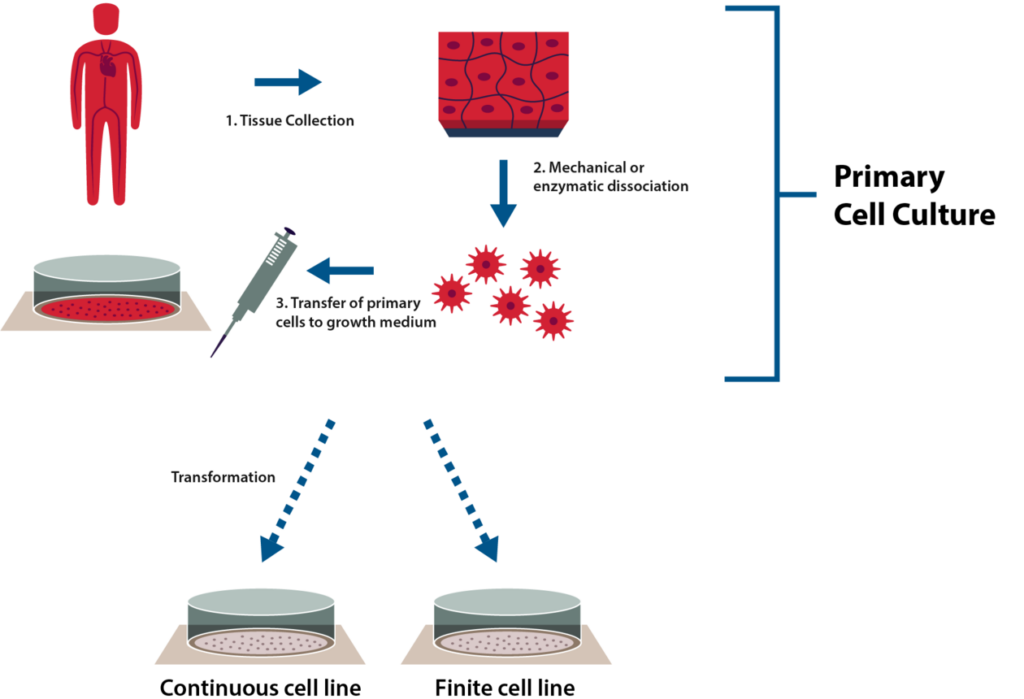
Primary cell cultures refer to the cultivation of cells that are directly isolated from human or animal tissues and processed to grow under controlled conditions in vitro. They represent the in vivo state of cells more closely than immortalized cell lines, giving the most biologically accurate data.
Other than being an outstanding model for studying cell physiology and biochemistry, primary cell culture has various applications in vaccine production, drug discovery, and gene therapy. Primary cell cultures also reduce the burden on animal models and make research cost-effective.
The most common primary cells used in research are epithelial cells, keratinocytes, fibroblasts, melanocytes, endothelial cells, muscle cells, immune cells, and mesenchymal stem cells. These are initially heterogeneous and can be maintained only for a finite time in vitro.
When primary cells undergo a genetic transformation, they divide indefinitely and become immortalized secondary cell lines. Since different cell types need different media to proliferate, it is important to optimize the culture conditions for each cell type (1,2).
Advantages of primary cells
– The use of human primary cells for research goals reduces the need of animal experiments thereby eliminating all the related ethical objections.
– With the cultivation of human primary cells, experiments on human material become possible, which otherwise could not have been done in vivo.
– Less reliance on animal experiments also means a reduction of experimental costs.
– Using primary cells sourced directly from human donors produces more reliable and relevant results and represents the in vivo biology of cells more closely.
Disadvantages of primary cells
– Primary cells take a much longer time to grow than immortalized cell lines. Moreover, they have limited growth potential and because of that even under optimal conditions, they eventually die.
– Cells derived from different donors behave differently to the same stimuli, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines.
– Though the costs of performing animal experiments are much higher than those of cultivating primary cells, solation costs are often very high.
– With subsequent passages, the characteristics of primary cells may change if optimum culture conditions are not maintained (3).
References
1. https://www.atcc.org/cell-products/primary-cells
2. Richter M, Piwocka O, Musielak M, Piotrowski I, Suchorska WM, Trzeciak T. From Donor to the Lab: A Fascinating Journey of Primary Cell Lines. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 22;9:711381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.711381. PMID: 34395440; PMCID: PMC8356673.
3. Segeritz CP, Vallier L. Cell Culture: Growing Cells as Model Systems In Vitro. Basic Science Methods for Clinical Researchers. 2017:151–72. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-803077-6.00009-6. Epub 2017 Apr 7. PMCID: PMC7149418.
