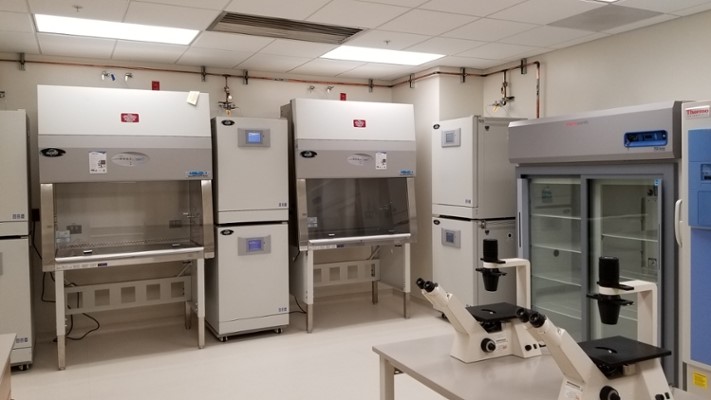
SET UP YOUR OWN CELL CULTURE LABORATORY
The continuous culture of eukaryotic cells has become a main-focused technique in several fields- biological, biochemical, and biomedical research. Cell culture needs a commitment of energy and resources to be undertaken in a professional manner. There is an ongoing need for culture facilities, several fundamental considerations such as ENVIRONMENT, LOCATION, VENTILATION, GASES, BASIC EQUIPMENTS to name a few.
Small cell culture facilities can be engineered without making major modifications to laboratory rooms. There are two major fundamental considerations that governs the would-be cell culture laboratory: CONTAMINATION AND SAFETY. The fundaments of cell culture owe much to the basic methods developed by microbiologists over past century. Eukaryotic cells are very sensitive to the primary and secondary metabolic products of microbes.
Bacteria and fungi are, hence, the biggest problem. Eukaryotic cells can also potentially harbor subcellular microbes that could cause diseases. It should also be noted that correctly locating a cell culture facility is of equal importance. The working environment needs to be clean, free from dust and easy to disinfect. Furthermore, thoughts must also be given to the how large and heavy equipment’s are to be bought in like laminar airflow. (1,2)
CELL CULTURE WOKRING SPACE: BASIC REQUIREMENTS AND LAYOUT
Many cell cultures can be maintained in buffered medium; however, some cells do not grow optimally in buffered medium but needs the buffering provided by the equilibrium of 5% CO2 with bicarbonate in the medium. This can be important for some specific cell lines and primary cultures. Ventilation and airflow in the cell culture environment are critical to operations.
At the simplest, there must be undisrupted airflow supply in the laminar hood, avoiding the circulation of dust and dirt. Ideally there should be no open windows. High efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters within the cabinets would ensure a good and sterile quality of working environment. (1) HEPA filters have 99.9-99.97% of efficiency, it also aids to improve the operations and the air quality under the cabinet.
To perform a basic range of cell culture procedures a list of equipment needs to be considered: such as laminar airflow cabinet, incubator, centrifuge, microscope, pipette set, micro-pipette, heamocytometer and freezer. (2) Apart from setting up the working space with all the instruments, a regular training, standard operating procedures, and centralized management of all aspects of cell culture would ensure economical, continuously monitored along with high standard of operations. (3)
The final thought would be to set up a sterile working environment suited for the cell cultures to grow, as they play a vital role in research studies.
REFRENCES:
1. CDC (1995). “Biosafety Cabinets; Primary Containment for Biohazards: Selection, Installation and Use of Biological Safety Cabinets,” 1st Ed. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington. Web edition http://www.niehs. nih.gov/odhsb/biosafe/bsc/bsc.htm
2. Freshney, R. I. (2000). “Culture of Animal Cells: A Manual of Basic Technique,” 4th Ed. Wiley-Liss, New York.
3. Doyle, A. (1998). “Cell and Tissue Culture: Laboratory Procedures” (A. Doyle, J. B. Griffiths, and D. G. Newell, eds.), Chap. 1. Wiley, Chichester.